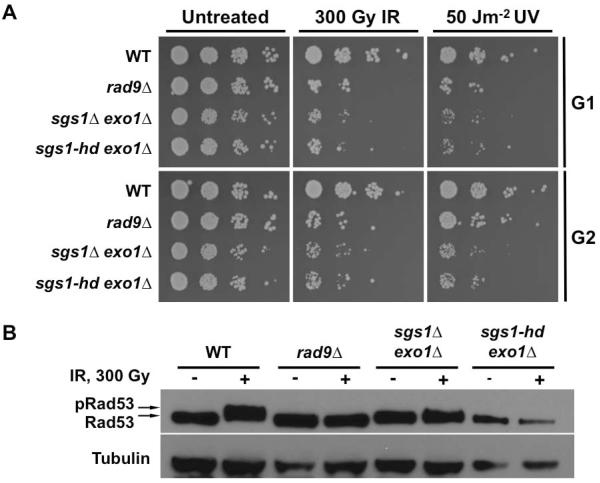
FIG. 3.
Catalytic function of Sgs1 is required for its role in G1 checkpoint. (A) Viability assay for DNA damaged G1 and G2 cells. Yeast cell cultures arrested with αF or nocodazole were treated with IR or UV. Ten-fold serial dilutions were spotted on solid media and then exposed to irradiation. All plates were incubated at 30°C for 2 days prior to image capture. (B) DNA damage-induced Rad53 phosphorylation. Cells expressing myc-tagged Rad53 and helicase-defective Sgs1 (sgs1-hd) in exo1Δ sgs1Δ background were arrested with αF and exposed to IR. Aliquots taken prior to and 15 min after irradiation were prepared for Western blot using NaOH. Rad53-myc was detected with anti-myc antibody while anti-tubulin antibody was used as a loading control. A mobility shift in the Rad53-myc band indicates phosphorylation.