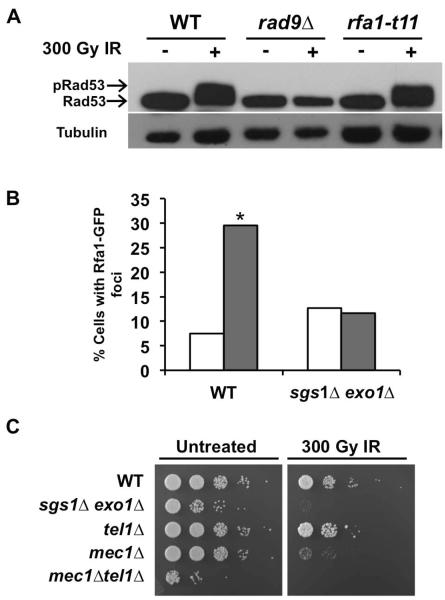
FIG. 5.
Sgs1 and Exo1 appear to interact with factors along the resection-dependent Mec1 activation pathway. (A) DNA damage-induced Rad53 phosphorylation. Cells expressing FLAG-tagged Rad53 and rfa1-t11 were used. Diluted overnight cultures were arrested with αF and exposed to IR. Aliquots taken prior to and 15 min after irradiation were prepared for Western blot using NaOH. Rad53-myc was detected with anti-FLAG antibody while anti-tubulin antibody was used as a loading control. A mobility shift in the Rad53-FLAG band indicates phosphorylation. (B) Rfa1-GFP foci formation in response to IR. WT and sgs1Δ exo1Δ cells were transformed with Rfa1-GFP plasmids. αF-arrested cultures were mock or IR-treated then resuspended in TBS. Number of G1 cells with foci was scored using confocal fluorescence microscopy. 100 cells were counted for each cell type and treatment (*, P< 0.05). White bars-0 Gy; Grey bars-300 Gy. (C) IR sensitivity of G1-arrested Mec1/Tel1 mutants relative to G1-arrested sgs1Δ exo1 cells. Overnight cultures of the indicated strains were diluted to 0.2 OD600 and arrested in G1 using αF (10 μM). Ten-fold serial dilutions were plated on solid media (YPD) and then exposed to IR (300 Gy) or mock-treated. Plates were incubated at 30°C for 2 days prior to image capture.