Figure 1.
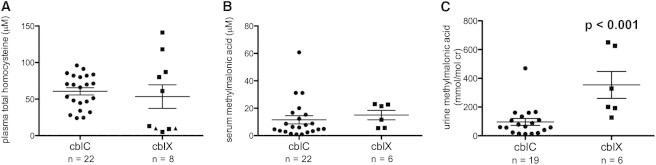
Metabolite Measurements in cblX Subjects Compared to Treated, Early-Onset cblC Subjects
Plasma total homocysteine (tHcy) and serum and urine methylmalonic acid (MMA) were measured in cblX subjects (single measurements) and 23 subjects with early-onset cblC deficiency (1–13 measurements per subject). In cases where multiple measurements were available for the same subject, the mean of all readings was used. n = the total number of subjects in each group.
(A) There was no statically significant difference in plasma tHcy measurements between cblC subjects and cblX subjects (cblC, 60.63 ± 4.88 μM; cblX, 64.25 ± 18.30 μM [mean ± SEM]). Normal levels of plasma tHcy are <13 μM. Triangles indicate two subjects with reportedly normal tHcy (no concentration was provided to the referring diagnostic laboratory).
(B) There was no significant difference in serum MMA measurements between cblC subjects and cblX subjects (cblC, 11.57 ± 2.99 μM; cblX, 15.00 ± 3.43 μM [mean ± SEM]). Normal levels of serum MMA are <0.4 μM.
(C) cblX subjects had higher urine MMA (t test p < 0.001) than did cblC subjects (cblC, 96.52 ± 23.89 mmol/mol creatinine; cblX, 354.20 ± 93.70 mmol/mol creatinine [mean ± SEM]). Normal levels of urine MMA are <4 mmol/mol creatinine.
