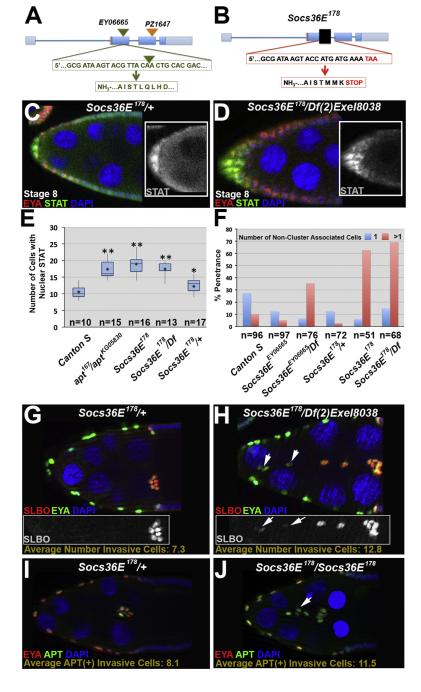
Fig. 3.
Loss of Socs36E increases STAT signaling and allows additional cells to become invasive. (A) Schematic of the Socs36E genomic locus, including previously described insertional alleles: Socs36EEY06665(green triangle) and Socs36EPZ1647(orange triangle). The gene and protein sequences flanking the Socs36EEY06665insertion are shown in green letters; the triangle indicates the insertion site. (B) Schematic of the Socs36E178allele. The black box is scaled to represent the approximately 500 base pairs deleted. The resultant gene and protein sequences are shown in the red boxes. (C–D) Control (C, Socs36E178/CyO) and Socs36E deficient (D) egg chambersstained with antibodies raised against EYA (red), which identifies anterior follicle cells, and STAT (green) depicts the increased range of nuclear STATprior to border cell migration in mutants. Insets: STAT antibody staining alone. (E) Box plotsquantifying nuclear STAT-positive anterior follicle cells at stage 8 in the indicated genotypes. Mean numbers for each are indicated by a diamond. Two-tailed t-tests compared Canton S and each respective genotype, where *=p<0.05; **=p<0.0001. (F) Quantification of the percentage of stage 10 egg chambers withone(blue) or more (pink)non-cluster associated invasive cells when Socs36E is disrupted. (G–H) Stage 10 egg chambers stained with antibodies directed against SLBO (red) and EYA (green). Insets show SLBO expression only. The average number of additional invasive cells is indicated. (G) HeterozygoteSocs36E178/CyOegg chambers have a wild type number of motile cells, which are clustered together at the oocyte. (H) When the Socs36E178allele is in trans to a deficiency for the locus, additional cells become invasive and do not cluster. Arrows indicate reducedSLBO expression in the non-cluster associated cells. (I–J) Stage 9 egg chambers stained with EYA (red) and APT (green) antibodies. The average number of APT-positive invasive cells is given. (I) A Socs36E178/CyO egg chamber displays a wild type number of motile cells. (J)Socs36E deficient egg chambers contain additional APT-positive non-cluster-associated invasive cells (indicated by arrow).