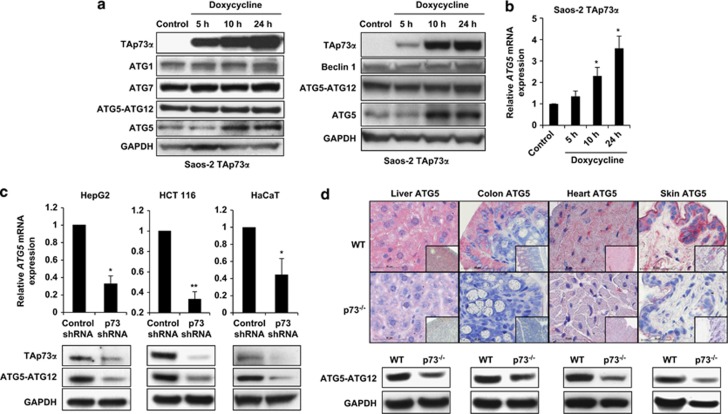
Figure 3.
p73 regulates ATG5 expression. (a) Immunoblotting. Saos-2 cells inducible for TAp73α were treated with doxycycline (2.5 μg/ml) for the indicated time periods. Expression levels of ATG1, ATG7, Beclin 1, monomeric ATG5, and the conjugated form of ATG5 (ATG5-ATG12) were investigated in two independent experiments. Increased levels of TAp73α resulted in increased monomeric ATG5 levels. TAp73β induction was associated with a slight increases of monomeric ATG5, whereas other members of the p53 family had no effect (see Supplementary Figure S10). (b) Quantitative real-time PCR. Saos-2 cells inducible for TAp73α were treated with doxycycline for the indicated time periods and ATG5 mRNA was measured. Values are means±S.D.s of three independent experiments. *P<0.05. (c) Quantitative real-time PCR (upper panel) and immunoblotting (lower panel). The indicated cells were treated with control shRNA and p73 shRNA. Values in the upper panel are means±S.D.s of three independent experiments. Reduced p73 expression was associated with reduced ATG5 expression at both mRNA and protein levels. p73 shRNA experiments were additionally controlled by real-time PCR (data not shown). (d) Immunohistochemistry (upper panel) and immunoblotting (lower panel). p73-deficient mice show significantly reduced ATG5 expression compared with WT mice. Bar, 50 μm. Original magnifications, × 630 and × 200 (lower right corners). Results are representative of three independent experiments