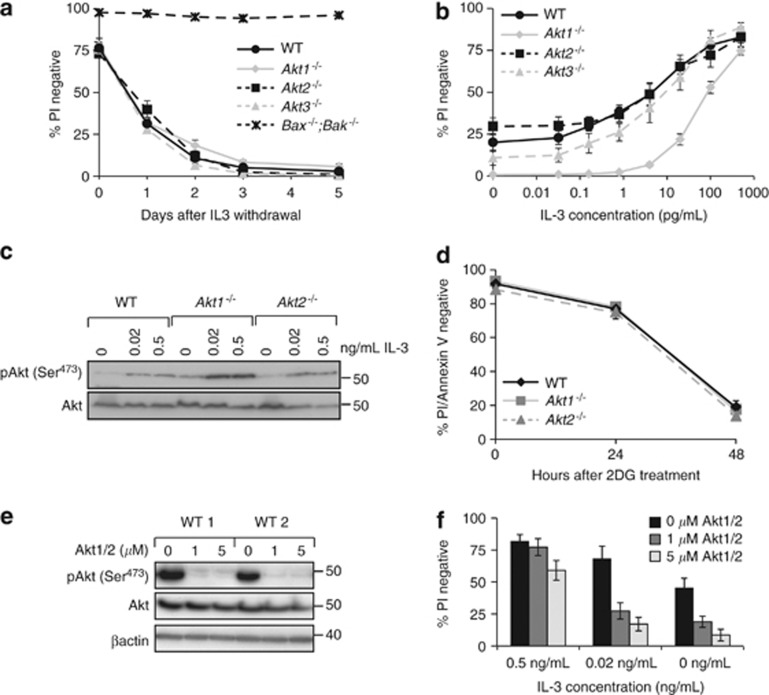
Figure 1.
Deletion of Akt1 reduces viability in limiting concentrations of IL-3. (a) Multiple independently generated clones of FDM cells of the indicated genotypes (n=number of clones; Akt1−/− n=3, Akt2−/− n=4, Akt3−/− n=4, WT n=4 and Bax−/−;Bak−/− n=2) were starved of IL-3 over 5 days. At the indicated time points, cell viability was determined by propidium iodide (PI) exclusion using flow cytometry. Data represent mean and standard error from three independent experiments using multiple clones. (b) Multiple independent clones of FDM cells of the indicated genotypes (Akt1−/− n=5, Akt2−/− n=4, Akt3−/− n=4 and WT n=4) were cultured at the indicated concentrations of IL-3 for 48 h. Viability was then determined by PI uptake using flow cytometry. Data represent mean and standard error, from three independent experiments over which all clones were tested. (c) Lysates from WT, Akt1−/−or Akt2−/− FDM cells cultured for 24 h in the indicated concentrations of IL-3 were probed with antibodies to phosphorylated Akt (serine 473) and total Akt. (d) WT, Akt1 or Akt2 null cells were treated with 3 mM 2-DG for 48 h. Cell viability was determined by PI uptake and Annexin V staining using flow cytometry. Data represent mean and standard error, from two independent experiments over which three clones of each genotype were tested. (e) Two independent WT clones were cultured in the presence of IL-3 and the AKT1/2 inhibitor (AKT1/2). Cell lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE and western blots probed with antibodies to detect phosphorylated Akt (serine 473), total AKT and β-actin as a loading control. (f) Three independent WT clones were cultured at the indicated IL-3 concentrations in the presence of AKT1/2. After 24 h, cell viability was determined by PI uptake using flow cytometry. Data represent mean and standard error, from two independent experiments using two clones in each experiment