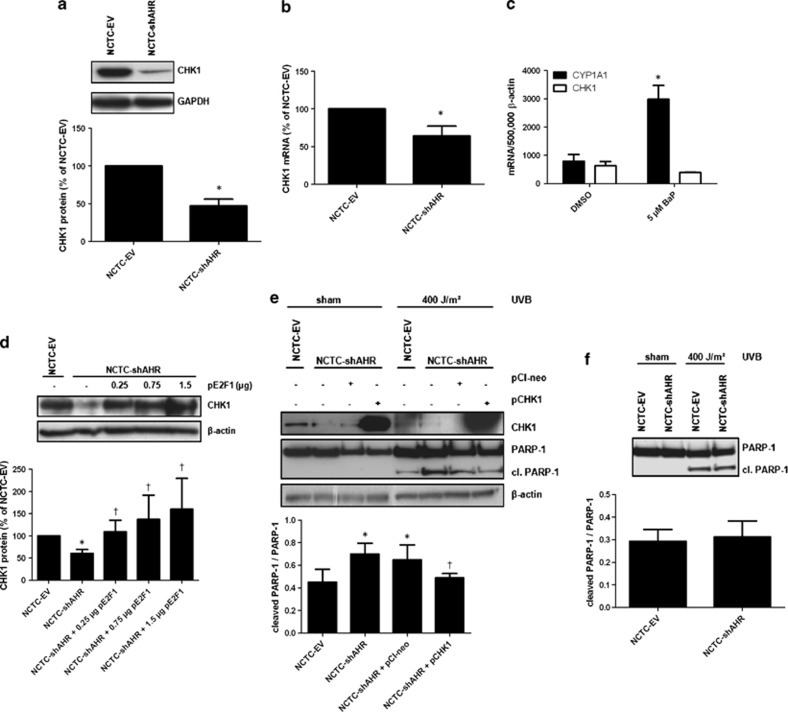
Figure 3.
Expression of CHK1 is diminished in NCTC-shAHR cells and causative for the enhanced susceptibility to UVB-induced apoptosis. (a) Protein expression of CHK1 and GAPDH in NCTC-EV and NCTC-shAHR KC. *Significantly reduced compared with NCTC-EV; (b) CHK1 mRNA expression was quantified by real-time PCR. Expression levels are given as fold of NCTC-EV. *Significantly reduced compared with NCTC-EV cells; (c) NCTC-EV KC were treated for 6 h with 5 μM BaP or 0.1% DMSO. CYP1A1 and CHK1 transcripts were determined by real-time PCR. *Significantly different from DMSO-treated NCTC-EV; (d) NCTC-shAHR KC were transiently transfected with indicated amounts of pE2F1. After 48 h, CHK1 and β-actin protein expression were determined. *Significantly reduced compared with NCTC-EV, †significantly increased compared with NCTC-shAHR; (e) NCTC-shAHR KC were transfected with 0.75 μg of the CHK1 expression vector (pCHK1) or empty vector pCI-neo. After 24 h, KC were irradiated with 400 J/m2 UVB, and additional 24 h later western blotting was performed using indicated antibodies. *Significantly increased compared with UVB-exposed NCTC-EV, †significantly decreased compared with UVB-irradiated pCI-neo-transfected NCTC-shAHR KC; (f) NCTC-EV and NCTC-shAHR KC were cultured in FCS-free medium for 24 h prior UVB irradiation (400 J/m2) to stop proliferation. After 24 h, protein was isolated and western blots were done using an anti-PARP-1 antibody that detects both PARP-1 and cleaved (cl.) PARP-1