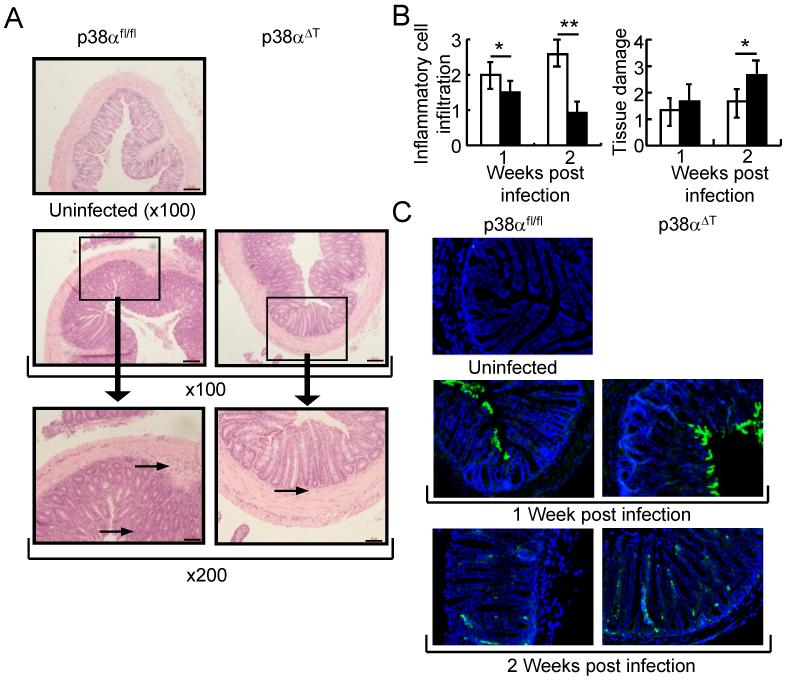
Figure 2. p38α in T lymphocytes regulates the bacterial clearance of C. rodentium-infected colon tissues.
(A) Inflammation in C. rodentium-infected mice. Colon tissues of C. rodentium-infected p38αfl/fl or p38αΔT mice were obtained after 1 week of infection and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Boxed area is X200 of the original X100 magnification. Arrows in the figure indicate inflammatory cell infiltration. Scale bar = 20 μm. (B) Histological analysis of the colon tissues of C. rodentium-infected p38αfl/fl or p38αΔT mice. After 1 or 2 weeks of infection, histological scoring of the infiltration of inflammatory cells and tissue damage was assessed (n=6). *, p<0.05, and **, p<0.01. Error bars indicate s.d. (C) Detection of C. rodentium in the colon tissues. Colon tissues specimens of infected mice were stained with anti-C. rodentium antibody (green) and nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Inflammation and bacterial staining of colon tissue of uninfected mouse are shown. Original magnification X100.