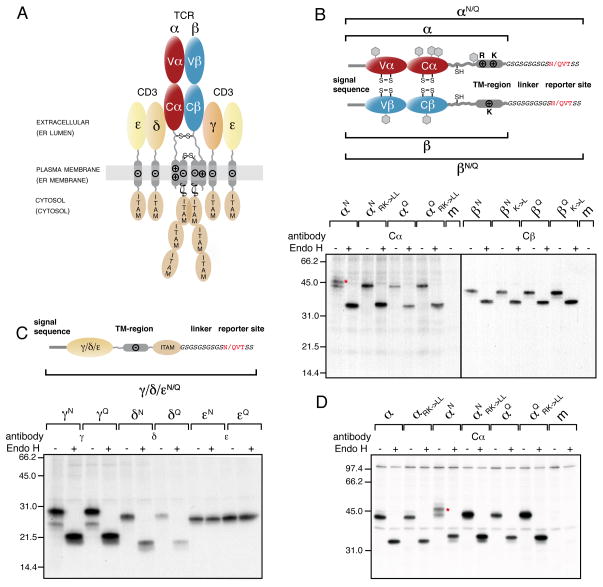
Figure 2. The TCR α-chain TM region is mislocalized into the ER lumen.
(A) The αβTCR consists of the clonotypic α- and β-chains, made up of one variable (Vα and Vβ, respectively) and one constant domain (Cα and Cβ, respectively) each and the co-receptor chains, CD3γ, δ and ε, as well as ζ. The receptor has three topological layers whose final disposition in the cell as well as their localization during the initial biosynthesis steps (shown in brackets) are indicated. Transmembrane basic (+) and acidic (−) residues and interchain disulfide bonds are shown. Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) initiate downstream signaling events upon TCR-MHC binding.
(B) Top: Outline and nomenclature of glycosylation reporter constructs to monitor ER-membrane integration of the TCR α- and β-chain. The engineered C-terminal glycosylation sites (NVT) and respective control sites (QVT) are marked in red. Predicted endogenous glycosylation sites are shown as grey hexagons. Bottom: Glycosylation analysis of radiolabeled TCR α- and β-chain reporter constructs in COS-1 cells. Mutations of the TM basic residues against Leu are indicated (RK->LL for the α-chain or K->L for the β-chain, respectively). Lysates from metabolically labeled cells were immunoprecipitated with antibodies specific for the human Cα or Cβ domains and treated with or without EndoH prior to SDS-PAGE analysis. The red asterisk marks the α-chain glycosylated at its C-terminal reporter site.
(C) Top: Schematics and nomenclature of analogous reporter constructs to monitor ER-membrane integration of the CD3γ, δ and ε chain. Bottom: Glycosylation analysis of radiolabeled CD3γ, δ and ε chain reporter constructs in COS-1 cells were performed as in (B) using the indicated chain-specific antibodies.
(D) Glycosylation analysis of radiolabeled TCR α-chain constructs in Jurkat J.RT-T3.1 cells. Nomenclature of the constructs is as in (B). The red asterisk marks the α-chain glycosylated at its C-terminal reporter site. Where indicated, radiolabeled proteins were deglycosylated with Endo H after immunoprecipitation with anti-Cα antibodies (m: mock transfection). See also Figure S2.