Figure 4. Identification of synthetic peptides to inhibit Fn attachment and invasion of HCT116 cells.
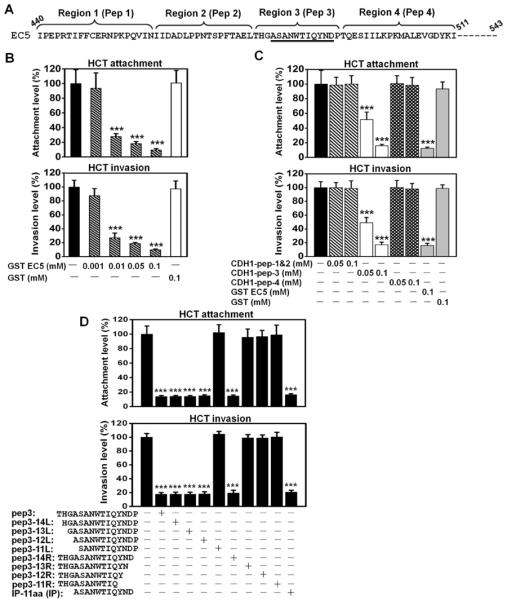
A. Partial amino-acid sequence of the EC5 domain. The regions and the corresponding peptides (pep) are shown above the sequence. The sequences corresponding to the inhibitory peptide (IP, see below) are underlined. Peptide 4 was the control peptide (CP) in all studies. B. Purified GST-EC5 fusion protein inhibits wild type Fn attachment and invasion of HCT116 in a dose-dependent manner. C. Fn attachment and invasion of HCT116 cells were inhibited by a synthetic peptide corresponding to region 3 (pep 3) on the EC5 domain, not by peptides corresponding to regions1&2, or 4. D. The inhibitory effects of synthetic oligopeptides carrying sequential deletions from the N- and C-termini of region 3 on Fn attachment and invasion. Deletion of 3 residues from N-terminal and 1 residue form C-terminal did not affect the inhibitory function. An 11-aa peptide (ASANWTIQYND) was found as the minimum sequence required for inhibition of Fn attachment and invasion. All values were expressed as relative to those without inhibition, which were designated as “100%”. The actual attachment and invasion levels were 6.3±1.4% and 1.6±0.1%, respectively, for B, and 5.9±0.7% and 1.4±0.1%, respectively, for C. The results are presented as mean±SD. ***p<0.001.
