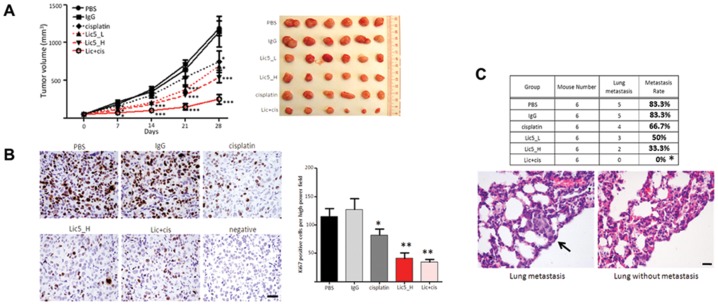
Figure 2. Antitumor and anti-metastatic properties of Lic5 in MHCC97L xenograft mouse model.
Treatment of tumor-bearing nude mice with Lic5 inhibits tumor growth and sensitizes tumors to cisplatin. HCC subcutaneous tumors were developed in nude mice using CDH17-expressing MHCC97L cells. Tumor-bearing nude mice were then injected with Lic5 alone, 2.5 mg/kg (Lic5_L) or 5 mg/kg (Lic5_H), or in combination of 1 mg/kg cisplatin (Lic+cis).Mice of the control group received mouse IgG (5 mg/kg). All mice were injected three times weekly for four consecutive weeks. (A) Sizes of the subcutaneous tumors were estimated weekly throughout the experimental period (left panel) and subcutaneous tumors were resected 28 days after the onset of treatment (right panel). Reduction in the sizes of the tumors was observed in single treatment group (Lic5 or cisplatin). Combined regimen of Lic5 and cisplatin (Lic+cis) could result a complete inhibition on tumor growth. All p-values were calculated using Student's t-test of GraphPad PRISM, for which 6 tumor samples were included in each group for comparison between control and treatment groups. *, p<0.05 and ***, p<0.001. (B) The level of proliferating cells in HCC xenografts was studied using immunohistochemistry. A significant reduction in the number of Ki67-stained cells was observed in xenografts of mice injected Lic5, alone and in combination with cisplatin. Original magnification, ×400; scale bar, 80 µm. *, p<0.01 and **, p<0.001. (C) Lic5 treatment of tumor-bearing nude mice decreases the chance of developing metastatic tumors in lungs. Any tumors grew in lungs were spotted by staining with hematoxylin and eosin in series of sections derived from lung specimens. Treatment of these mice using Lic5 reduced the percentage of mice having metastatic tumors in lungs and the most significant effect was observed in combined treatment group with Lic5 and cisplatin. Chi-squared test was applied to compare control group with all other groups. *, p<0.05. Original magnification, ×400; scale bar, 40 µm.