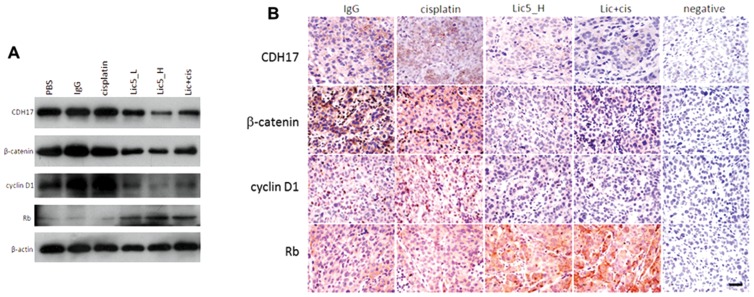
Figure 3. Lic5 treatment inactivated Wnt/β-catenin signaling in HCC tumors.
Mice having MHCC97L-derived tumors were subjected to single or combined treatment of Lic5 and cisplatin as in Fig. 2. (A) Changes in the protein level of Wnt/β-catenin pathway components like β-catenin, cyclin D1 and retinoblastoma (Rb) in resected HCC tumors were detected using western blot. Suppression of CDH17 level using Lic5 accompanied with an inactivation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway, leading to reduction in the levels of β-catenin and cyclin D1 and induction in the level of Rb. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (B) Similar trend in the changes of the levels of β-catenin, cyclin D1 and Rb was observed in tissue sections of the HCC tumor xenografts using immunohistochemistry. Original magnification, ×400; scale bar, 80 µm.