Figure 8. PP1β knockdown blocks convergence and extension but does not alter mesodermal cell fate or dorsal-ventral patterning.
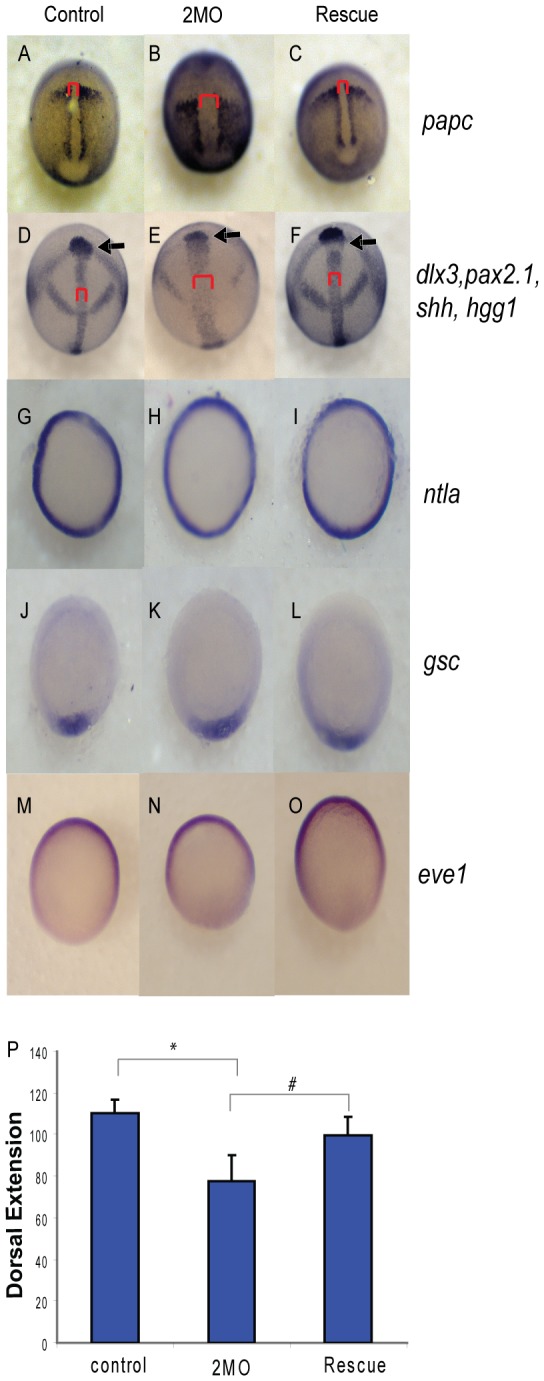
Embryos injected with either 1.5 ng of the 2 MO cocktail (0.75 ng ppp1cba MO and 0.75 ng of ppp1cbb MO) or 1.5 ng of the cocktail with 200 pg of ppp1cbb mRNA (rescue) were grown alongside uninjected clutch-mates (control) and staged and fixed for in situ hybridization. Embryos at 90% epiboly were fixed and stained with (A–C) papc (presomitic mesoderm) and imaged from an angle approximately 30 degrees from dorsal to allow visualization of the prechordal plate (marked with an arrow). Embryos at bud stage stained with hgg1 (to mark the prechordal plate), shh (midline), pax2.1 (midbrain-hindbrain boundary) and dlx3 (neural plate) (D–F) and imaged with a view from dorsal. The red bracket marks the width of the notochord and the black arrow points to the prechordal plate. Embryos at 50% epiboly were stained with ntla (G–I) to assay for mesoderm induction, gsc to assay for dorsal cell fates (J–L) and eve1 (M, N, O) for ventral cell fates, all viewed from the animal pole, with dorsal facing down. (P) Quantification of body axis elongation at bud stage for embryos injected with the indicated reagents. Each injection experiment was performed at least 3 times and the morphogenetic measurements were performed on 50 48 hpf and 50 bud stage embryos. Error bars are standard error and a black * indicates a statistically significant difference from control and a # indicates a statistically significant rescue compared to morpholino injected embryos. Statistical significance was calculated using a one-factor ANOVA with Tukey post hoc analysis and is defined as p < 0.05.
