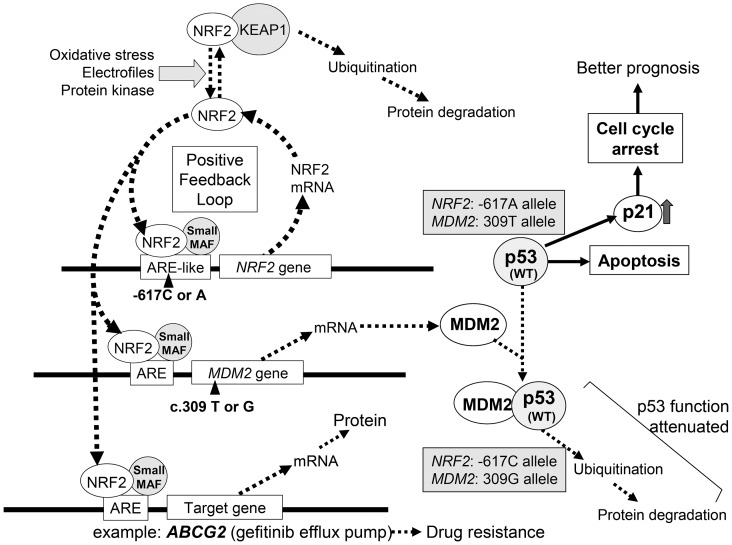
Figure 3. Schematic illustration showing the effect of NRF2 SNP–617C>A and MDM2 SNP c.309 T>G on the p53-mediated suppression of cancer cell proliferation and drug resistance.
In response to oxidative stress, electrophiles challenge, or protein kinase-mediated phosphorylation (e.g., via the PI3K-Akt pathway), the NRF2 protein is released from KEAP1 and then translocated into the nuclei. The SNP–617C>A in the ARE-like motif is considered to play a role in the positive feedback loop of transcriptional activation of the NRF2 gene. The SNP homozygote (–617 A/A) significantly attenuates the positive feedback loop and also expression of NRF2-target genes, such as MDM2 and ABCG2. In the case of MDM2 gene expression, the SNP (c.309 T>G) in the first intron of the MDM2 gene increases the binding affinity toward Sp1 and results in higher expression levels of MDM2 protein. MDM2 protein, thus highly expressed, binds to p53 (wild type; Wt) protein and leads to ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of p53 (Wt) protein. Combination of the 309G (SNP) allele of the MDM2 gene and the –617C (Wt) allele of the NRF2 gene may have negative impacts on p53 (Wt)-mediated tumor suppression. On the other hand, lung cancer patients harboring both the 309T (Wt) allele of the MDM2 gene and the –617A (SNP) allele of the NRF2 gene may have better prognosis due to the tumor suppressor function of p53 (Wt), such as apoptosis and p21WAF1/cip1-mediated cell cycle arrest. Expression of the ABCG2 gene is known to be up-regulated by NRF2. Gefitinib, an inhibitor of EGFR tyrosine kinase, is extruded by ABCG2 out of cancer cells. Thus, NRF2-mediated induction of ABCG2 expression can confer cancer cells with acquired resistance to gefitinib and other anticancer drugs.