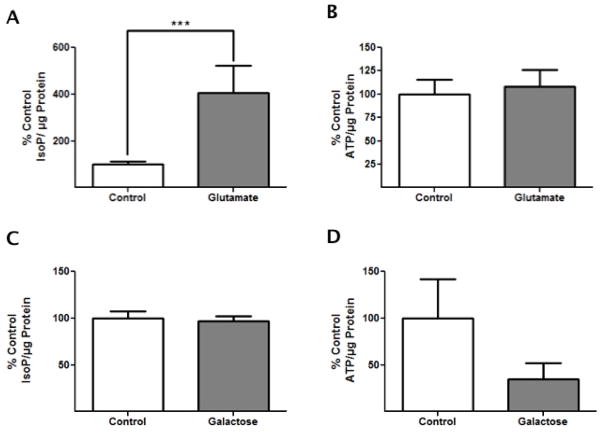
Figure 4. Galactose Challenge Induces an Energetic Stress While Glutamate Toxicity Induces an Oxidative Stress.
HT-22 cells were exposed to either 3 mM glutamate for 24 h or 72 h 25 mM galactose and were either harvested and prepared for F2t-IsoP measurements or incubated with Nucleotide Releasing Agent for ATP measurements. (A) The amount of F2t-IsoPs normalized to total protein in glutamate-treated cells differs significantly from control cells, demonstrating that glutamate toxicity induces oxidative stress (n=6, ***p<0.05). (B) The amount of ATP normalized to total protein in glutamate-exposed cells does not differ from control cells, showing no change in energetic status after glutamate toxicity (n=5, p>0.05). (C) In galactose- treated cells, the amount of F2t-IsoP did not differ significantly from control cells, demonstrating limited oxidative stress due to galactose challenge (n=4, p>0.05). (D) The amount of ATP normalized to total protein in galactose-treated cells was less than that of control cells; however, the difference was not significant (n=5, p>0.1). The data were analyzed for significance using tailed t-tests.