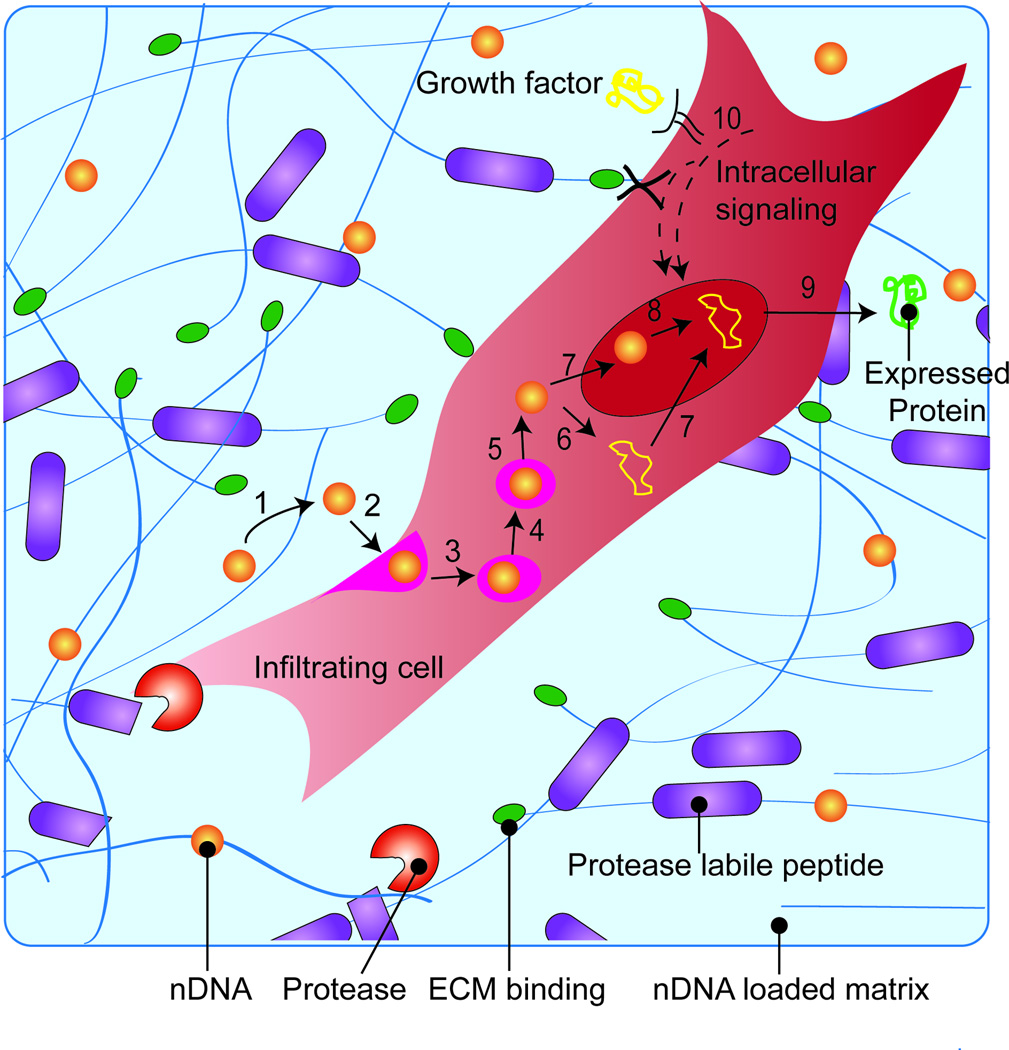
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of protein expression. For gene delivery, nDNA (1) is released from the scaffold through either hydrolysis or cellular migration (2) and internalized into the endosome (3). The endosome matures changing its oxidative and acidity resulting in endosomal escape of nDNA (4–5). nDNA can enter the nucleus (7) to be unpacked (8) or be de-coupled in the cytosol (6) for nuclear entry (7), where transcription and translation occurs (9) for protein expression. Growth factors or other bioactive signals can be used to induce intracellular signaling pathways that prime cells for transfection (10).