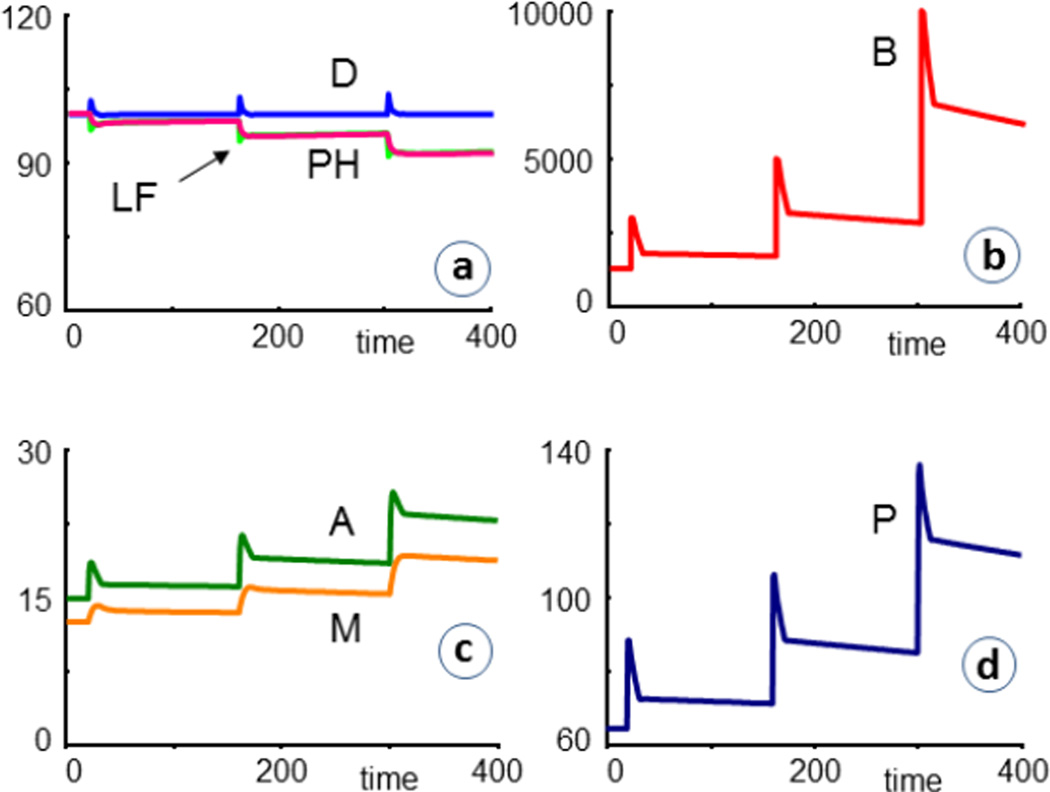
Fig. 6.
Simulation results of cystic fibrosis patients (CF = 1) that are repeatedly infected and receive antibiotics for ten days, starting shortly after each infection (AB = 5 during time periods 22–32, 162–172, 302–312). The bacterial load is substantially decreased, but the percentage of remaining healthy cells (PH) and the lung function (LF) at t = 400 are not all that much improved (PH = 92.2 with antibiotics versus 90.6 without). For an antibiotic with doubled efficacy (AB = 10), the trends are very similar, and the final the value is PH = 94.2.