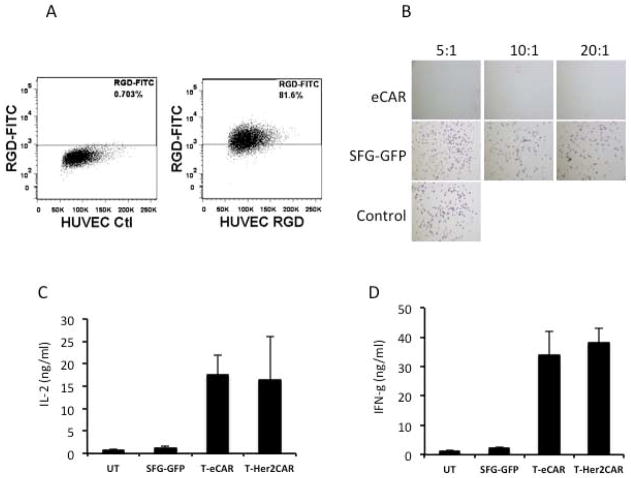
Fig. 2. Cytolytic effect of T-eCAR against HUVEC.
A. Flow cytometry analysis of αvβ3 expression on HUVEC. HUVECs were stained with FITC-conjugated RGD peptide before they were analyzed by flow cytometry. B. Cytolysis of HUVEC by T-eCAR. Splenocytes obtained from C57BL/6 donors were transduced with retroviruses containing either eCAR (T-eCAR) or the control SFG-GFP construct, in which the echistatin was replaced with the GFP gene. The cells were then mixed with HUVEC at the indicated ratio for 24 h. Then the T cells in suspension were removed by washing and the remaining cell monolayer was stained with crystal violet to determine cell viability. The control well represents HUVEC alone. Note that live cells are positively stained. C. Quantification of IL-2 release during T-eCAR and T-Her2CAR mediated killing of target cells. D. Quantification of IFN-γ release during T-eCAR and T-Her2CAR mediated killing of target cells.