Fig. 4.
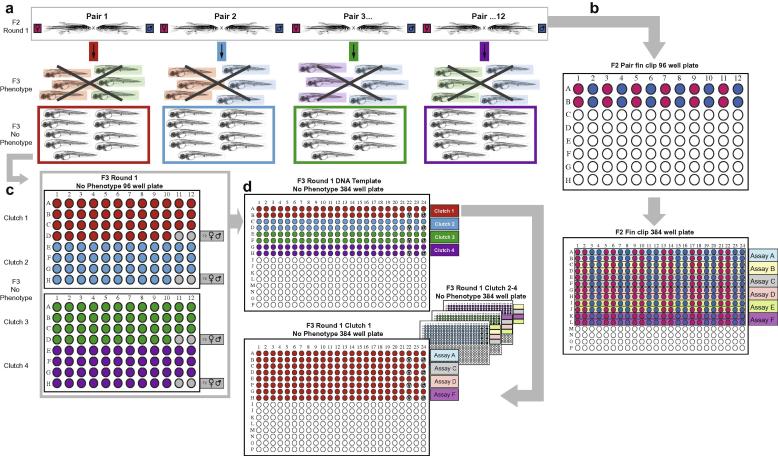
Multi-allelic phenotyping – round 1. F2 families are randomly in-crossed and the 12 largest clutches are collected and enter the pipeline with their respective parents. 150–200 fertilized F3 embryos are raised till 5 dpf, all abnormal fry are removed and 46+ phenotypically normal fry are collected and frozen in MeOH. (a) Fin clips are taken from each F2 parent and placed into a 96 well plate. Genomic DNA is prepared from the tissue and transferred into 384 well plates allowing for up to 24 KASP™ genotyping assays per 384 well plates, with all disruptive mutations identified in the original F1 male being interrogated. (b) The 46 phenotypically normal embryos from each clutch are aliquoted into half of a 96 well plate, DNA is extracted, and aliquots of the corresponding parental DNA are added to the last two wells. (c) The 96 well plates are transferred into 384 well plates and each clutch is stamped out into an individual 384 well plate and assayed for all alleles that both parents were heterozygous for (d).