Figure 4.
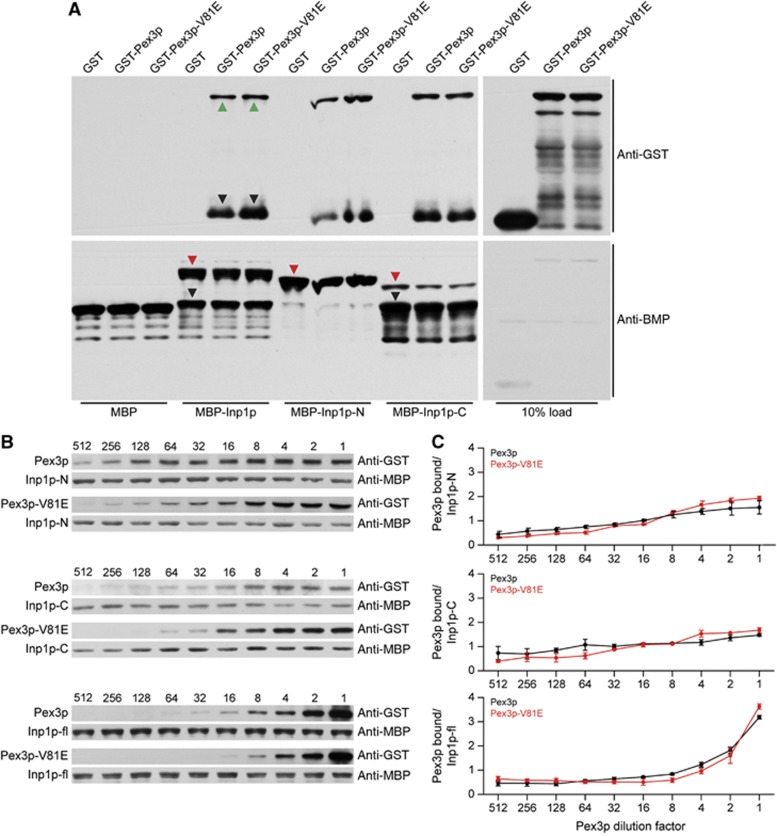
The V81 residue of Pex3p is not required for direct binding of Inp1p. (A) MBP alone or MBP–Inp1p fusions immobilized to amylose beads were incubated with extracts of E. coli synthesizing GST, GST-Pex3p, or GST-Pex3p-V81E. Bound proteins were detected by immunoblotting with anti-GST antibody (upper panel). Total MBP fusion proteins were visualized by immunoblotting with anti-MBP antibody (lower panel). Inp1p-N and Inp1p-C are N-terminal (a.a. 1–280) and C-terminal (a.a. 281–420) fragments of Inp1p. Red triangles indicate full-length MBP fusions, green triangles indicate full-length GST fusions, and black triangles indicate degradation products. (B) Equimolar amounts of purified recombinant MBP–Inp1p, MBP–Inp1p-N, and MBP–Inp1p-C were coupled individually to amylose beads and incubated with serial dilutions of E. coli lysates containing GST-Pex3p or GST-Pex3p-V81E. Dilution factors are denoted above immunoblots. GST- and MBP-fusion proteins were detected as in (A). (C) The ratio of bound Pex3p or bound Pex3p-V81E to Inp1p obtained by densitometric analysis of the bands in (B) was plotted against the Pex3p-dilution factor. The means±s.e.m. of three independent experiments are presented.
Source data for this figure is available on the online supplementary information page.