Figure 5.
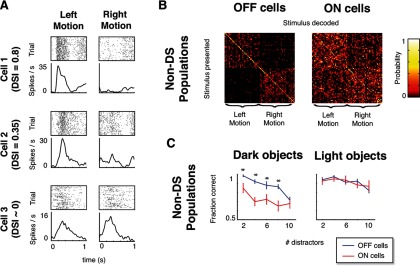
Performance in the CM task does not rely on DS responses of individual cells. A, Rasters (80 trials) and smoothed firing rates for example cells that are highly DS (top), mildly DS (middle), and non-DS (bottom) for leftward versus rightward motion. Data cover the interval over which direction selectivity was calculated, i.e., the period during which a single moving object passed over the cell's receptive field. B, Confusion matrices calculated for populations of non-DS (DSI < 0.3) RGCs (for dark CM stimuli with 4 stationary distractors) are similar to those calculated from the complete populations (compare Fig. 2C): OFF non-DS populations were able to signal motion direction, whereas ON non-DS cells were not. C, Non-DS population performance matched the complete population performance across task difficulties: ON non-DS populations performed poorly in the dark-object CM task, whereas OFF non-DS populations performed well in the light- and dark-object CM tasks (compare Fig. 3C). Asterisks (significance) and error bars were calculated as in Figure 3C.