Figure 3.
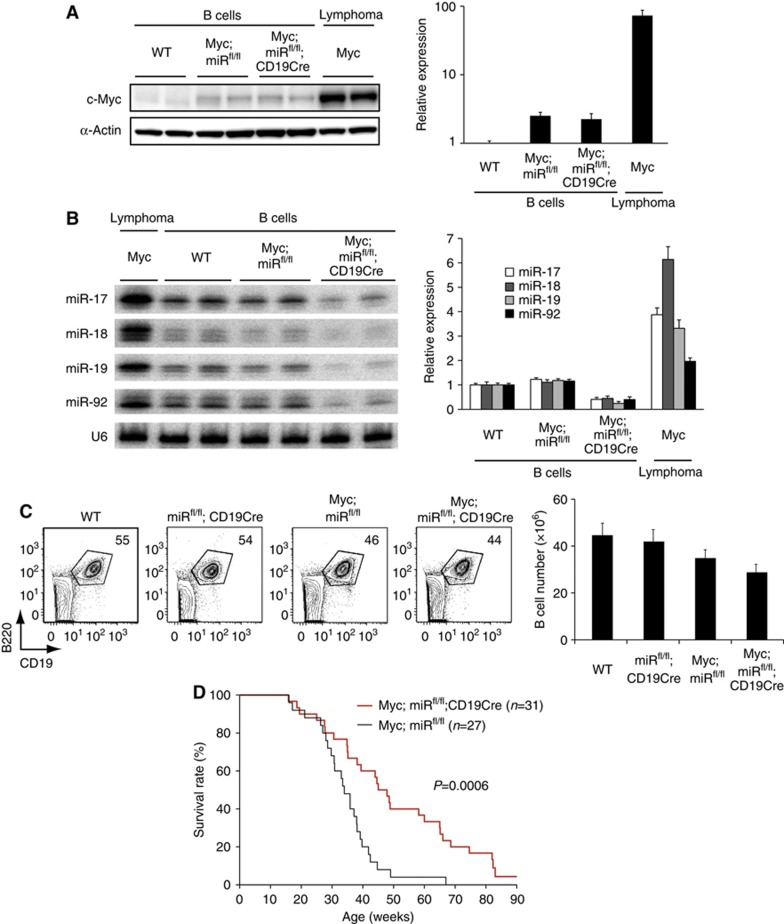
Genetic ablation of the miR-17∼92 gene delays Myc-mediated lymphomagenesis. (A, B) The c-Myc protein (A) and miR-17∼92 (B) expression levels in B cells purified from 2–3-month-old mice of indicated genotypes and lymphoma cells purified from λ-Myc mice were determined by western (A) and northern (B) blot analysis, respectively. Left panels show representative blots, and right panels summarize quantification results from three independent experiments (n=5–8 in each group for western blot and n=6∼14 in each group for northern blot). The c-Myc/β-actin and miR/U6 ratios in WT B cells were arbitrarily set as 1. The residual bands in Myc;miRfl/fl;CD19Cre B cells in (B) are likely from cross-hybridization with miRNAs encoded in the two homologous clusters, miR-106a∼363 and miR-106b∼25. (C) Flow cytometry analysis of splenocytes of 2-month-old mice of indicated genotypes (n=5–10 in each group). Splenic B cell (B220+CD19+) numbers are summarized in the right panel. (D) Kaplan–Meier survival curves of 31 Myc;miRfl/fl;CD19Cre and 27 littermate control Myc;miRfl/fl mice. The P-value was determined by Mantel–Cox logrank test.
Source data for this figure is available on the online supplementary information page.