Figure 2. BRCA1 location determines ABT-888 induced cytotoxicity.
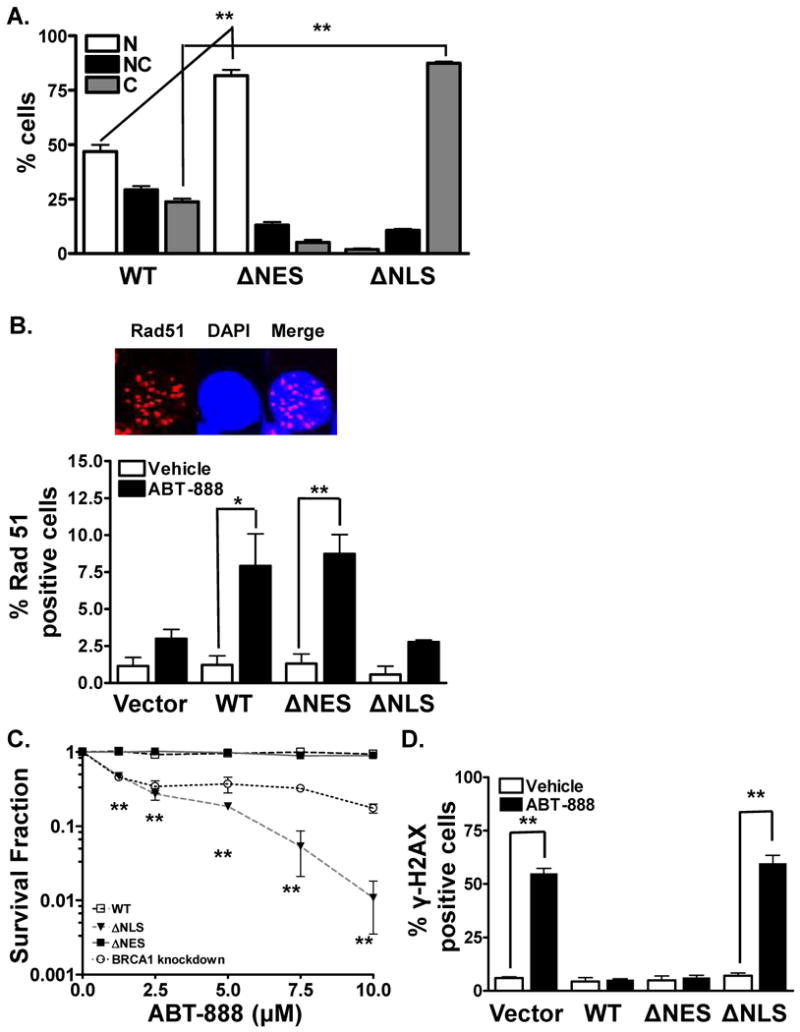
(A). BRCA1 location mutants are located predominantly either in the nucleus or the cytosol. MCF7 BRCA1 shRNA cells were transfected with either WT-BRCA1 YFP, NLS-BRCA1 YFP (cytosolic BRCA1) mutant, or NES-BRCA1 YFP (nuclear BRCA1) mutant. BRCA1 distribution was analyzed via immunohistochemical staining for YFP. NES-BRCA1 mutant was exclusively located in the nucleus whereas NLS-BRCA1 mutant was located in the cytosol. Shown is the representative data of three independent experiments (mean ± SEM, **p < 0.001). (B). Cytosolic BRCA1 mutant abrogates HR-mediated DSB repair. 16 hours following transfection with the various BRCA1 mutants, MCF7 BRCA1 shRNA cells were exposed to 10μM ABT-888. 24 hours following the drug treatment, Rad51 foci levels were analyzed via immunohistochemistry. A robust induction in Rad51 foci was observed in WT-BRCA1 and NES-BRCA1 mutant cells. No significant induction in foci formation was observed in the NLS-BRCA1 mutant or the vector alone, indicative of deficient HR-mediated repair. Shown is the representative data of three independent experiments the percent of cells (mean ± SEM) with Rad51 foci (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.001). Inset, a representative staining of cell exhibiting Rad51 foci (red) with the nucleus stained with DAPI (blue). (C). Cytosolic BRCA1 augments breast tumor response to PARP inhibition. MCF7 BRCA1 shRNA cells were transfected with the various mutants and subsequently sorted for YFP. 24 and 48 hours following transfection, cells were exposed to various doses of ABT-888. ABT-888 significantly attenuated the colony formation ability of NLS-BRCA1 mutant expressing breast cancer cells compared to vehicle alone. In contrast, no significant increase in cytotoxicity was observed in WT-BRCA1 and NES-BRCA1 mutant expressing cells. Shown is the representative data of at least three independent experiments (mean ± SEM, **p < 0.001). (D). Absence of BRCA1 or cytosolic BRCA1 increases γ-H2AX foci in human breast cancer cells. MCF7 BRCA1 shRNA cells were transfected with the various mutants of BRCA1. 40 hours following transfection, cells were treated with vehicle or 10μM ABT-888. 24 hours following the treatment period, cells were assessed for γ-H2AX foci. A robust induction in γ-H2AX foci was observed with ABT-888 treatment in the NLS-BRCA1 mutant or vector expressing cells, indicative of increased DNA damage. On the contrary no significant induction in foci formation was observed with ABT-888 treatment in the NES-BRCA1 mutant or WT-BRCA1 expressing cells, indicative of lack of DNA damage. Shown is the representative data of three independent experiments the % of cells (mean ± SEM) with >10 foci (**p < 0.001).
