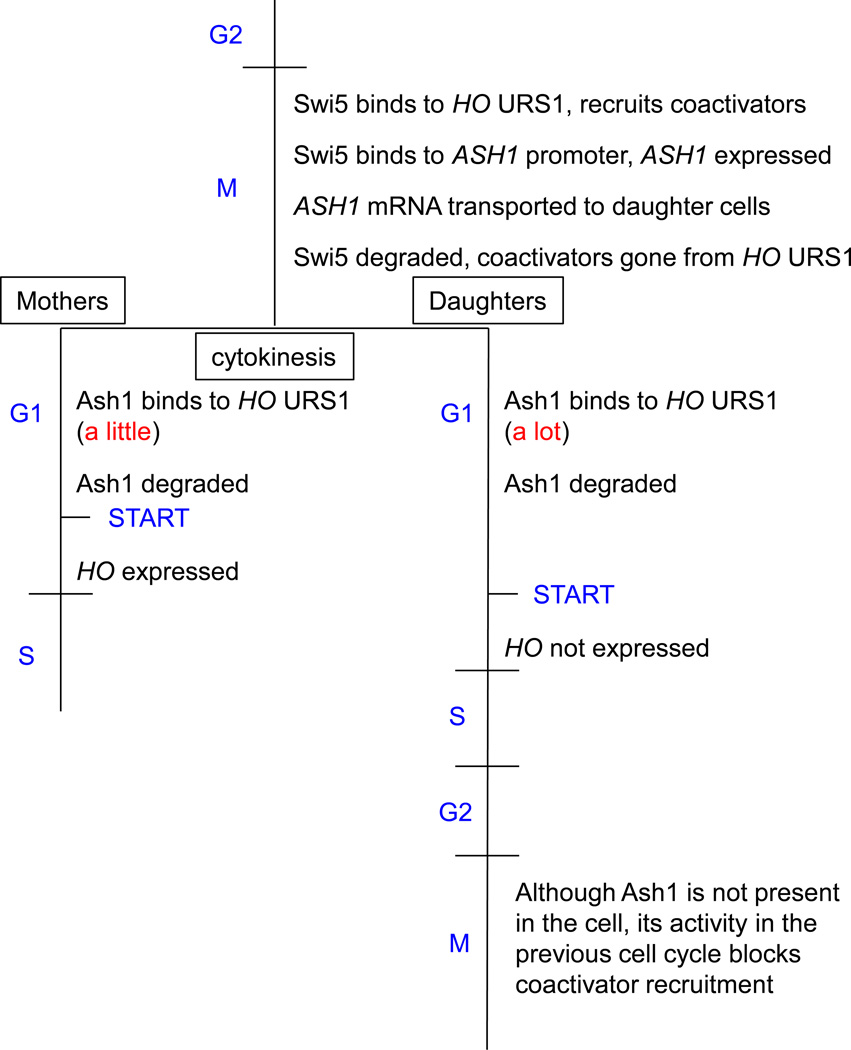
Fig. 3. Ash1 repression at URS1 persists from the previous cell cycle.
During G2 phase Swi5 binds to HO URS1, recruiting coactivators that alter URS1 chromatin. Concurrently, Swi5 binds to the ASH1 promoter, and the expressed ASH1 mRNA is transported to daughter cells and translated. Swi5 is quickly degraded ending the coactivator presence at URS1. Ash1 binds to URS1 after cytokinesis, and is quickly degraded. Thus, the effects of Ash1 revealed through genetic analysis, occur in the second M phase, whereas Ash1 was bound to the promoter much earlier in the cell cycle. START, in late G1, refers to the commitment point for the G1/S transition