Fig. 1. Disease-associated variation is concentrated in DNase I hypersensitive sites.
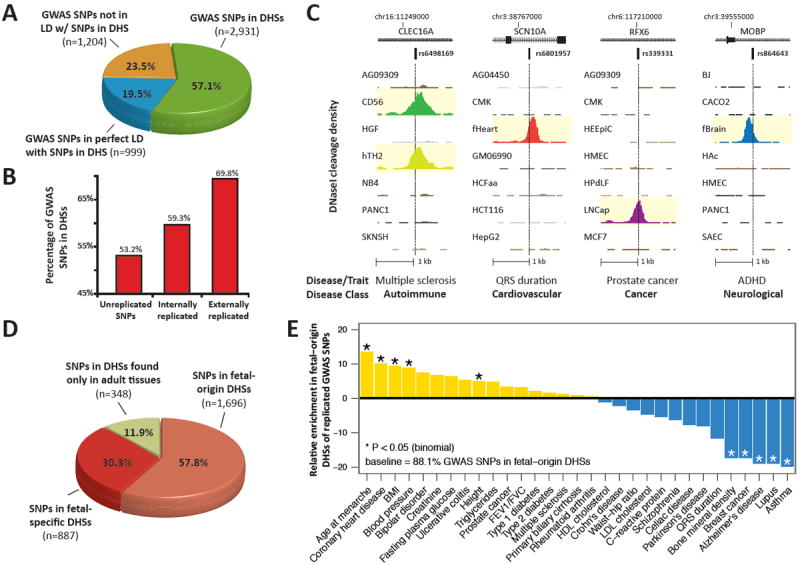
(A) Proportions of noncoding GWAS SNPs localizing within DHSs (green); in complete linkage disequilibrium (r2 = 1) with a SNP in a DHS (blue); or neither (yellow). Note that 76.5% of GWAS SNPs are either within or in perfect LD with DHSs. (B) Proportions of GWAS SNPs overlapping DHSs after partitioning by degree of replication. (C) Representative DNase I hypersensitivity (tag density) patterns at diverse disease-associated variants. (D) Proportion of GWAS SNPs localizing in DHSs active in fetal tissues that persist in adult cells (salmon); fetal stage-specific DHSs (red); and adult stage DHSs (green). (E) GWAS SNPs in DHSs show phenotype-specific enrichment for fetal regulatory elements.
