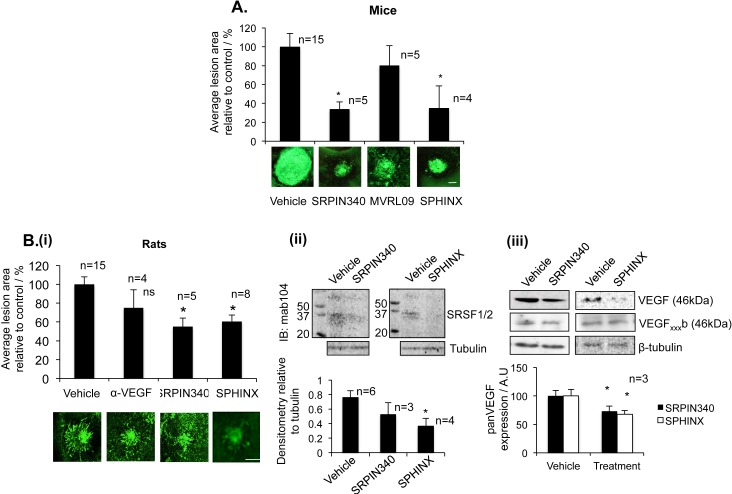
Figure 3.
SRPK inhibitors are antiangiogenic. (A) Fifteen C57/B6 mice were subjected to laser photocoagulation (IRIDEX Oculight GLX λ, 810 nm, 250 mV, 0.1 second, 75 μm, 4 lesions/eye). On day 0 and day 7 mice received an intraocular (i.o.) injection of SRPIN340, MVRL09, SPHINX (10 ng, 5 ng/μL–2 μL), or saline in the control eye. SRPIN340 and SPHINX both significantly reduced neovascular growth compared with saline-injected controls. Scale bar: 100 μm. (Bi) Norway Brown rats, after induction of CNV, were injected with either 25 ng (10 ng/uL) SRPIN340, 25 ng (10 ng/ul) SPHINX, 1 μg of the anti-mouse VEGF antibody, and saline in the control eye directly after laser procedure (day 0) and on day 7. Staining with isolectin-B4 of the RPE-choroid-sclera complex showed a decrease in lesion size for anti-VEGF and a significant decrease with SRPIN340 and SPHINX. Examples of lesions are shown. Scale bar: 200 μm. (P < 0.05, One-way ANOVA, Bonferronni post hoc). N, number of eyes. (Bi-i-iii) Rats were culled on day 4 (for protein). Protein extracted from retinae four days after laser induction was subjected to Western blot for phospho-SR proteins (Bi-i) or panVEGF (A20) (Bi-ii). SPHINX significantly reduced SRSF1/2 phosphorylation and both SRPIN340 and SPHINX significantly reduced the expression of total VEGF in the retina compared with saline injected eyes, but failed to alter the expression of VEGFxxxb isoforms.