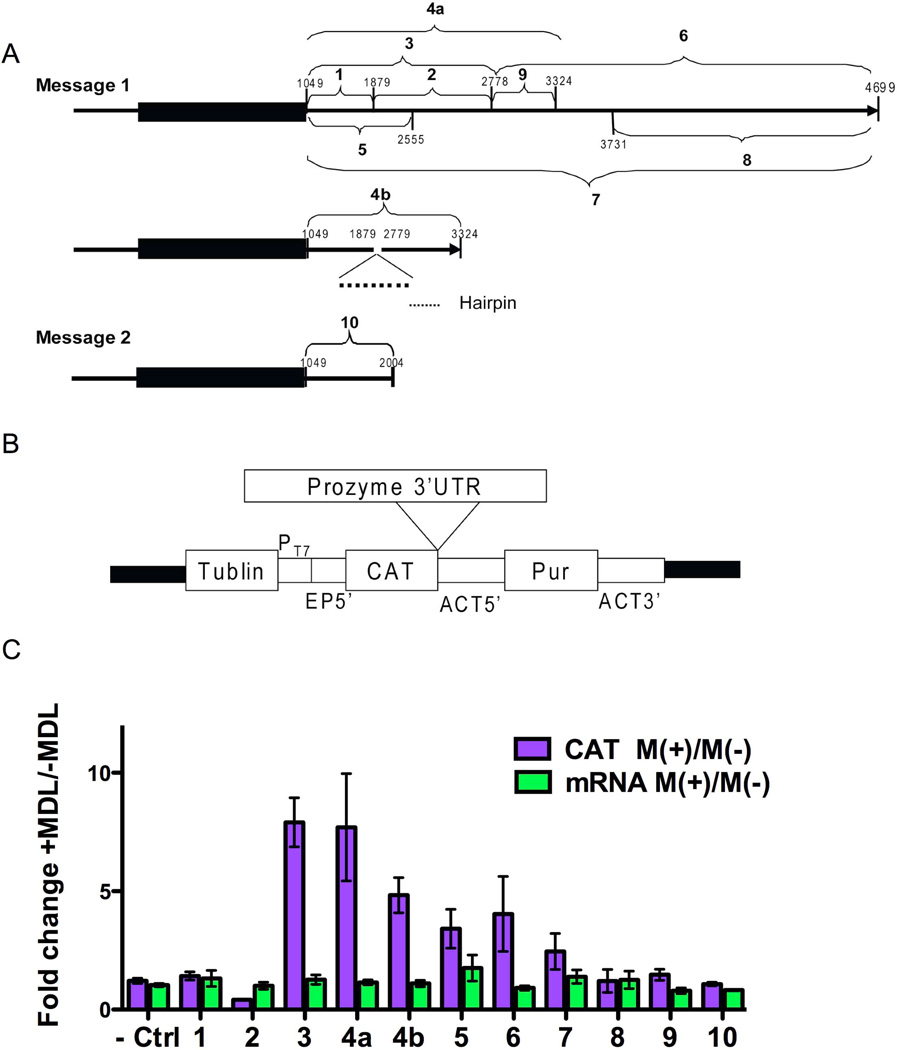
Figure 2. The effect of AdoMetDC inhibition on CAT expression levels from prozyme 3’UTR reporter constructs.
(A) Schematic of the prozyme 3’UTR fragments that were cloned into pHD1437 reporter construct vector. Number (from 1 to 10) indicates the fragment number and subsequent construct number. Nucleotide positions are displayed. The start and end points of each fragment are shown in Table 4S. The gene is numbered with position 1 representing the first gene specific base after the splice leader in the 5’UTR (Figures S1 and S2) (B) Structure of the reporter gene vector pHD1437: the black line of the structure of pHD1437 shows the plasmid backbone. Other components include a region from the tubulin locus (Tublin), a T7 polymerase promoter (PT7), a 5’-splice site and UTR from EP1 gene (EP5’), a CAT reporter gene (CAT), 5’UTR from the actin locus (ACT5’), a puromycin selectable marker gene (Pur), and the actin 3’UTR (ACT 3’). (C) CAT reporter plasmids containing different prozyme 3’UTR fragments were transiently transfected into BSF 90–13 cells. The empty pHD1437 vector was transfected as the control (Ctrl). Cells were grown for 3 h before the addition of MDL 73811 (75 nM), and then incubated for additional 16 h before harvesting. The CAT ELISA assay was used to determine the level of CAT enzyme activity (CAT), and mRNA levels were quantitated by qPCR with primers from table 3S (mRNA). The fold change was calculated as M(+)/M(−). Errors represent the standard error of the mean for n=3–4 independent biological replicates.