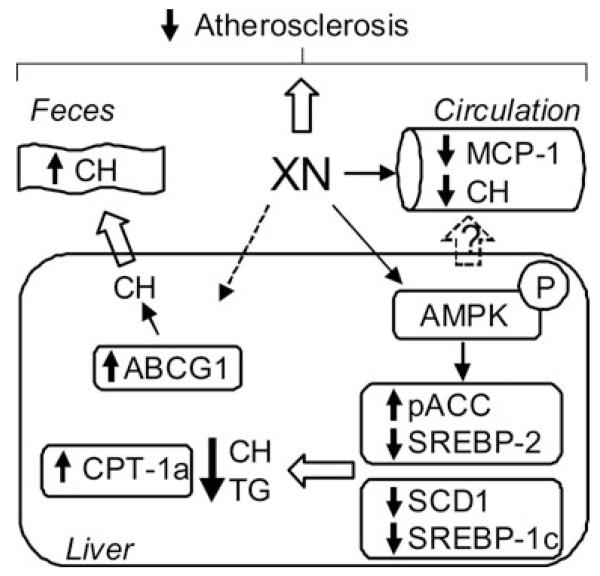
Figure 7.
Schematic summary of the effects of XN feeding to ApoE−/− mice. XN administration leads to phosphorylation of hepatic AMPK, which phosphorylates and inactivates ACC, reduces mature SREBP-2 protein and decreases mRNA expression of SREBP-1c and SCD1. In addition, increased expression of CPT-1a suggests increased fatty acid beta-oxidation. As a consequence, de novo lipogenesis in the liver is reduced and fecal cholesterol content is increased. In combination with reduced cholesterol and MCP-1 concentrations in the circulation, XN attenuates atherosclerotic plaque formation in WTD-fed ApoE−/− mice. ABC, ATP-binding cassette transporter; ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; CH, cholesterol; CPT, carnitine palmitoyltransferase; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; SREBP, sterol regulatory element-binding protein; TGs, triglycerides; XN, xanthohumol.