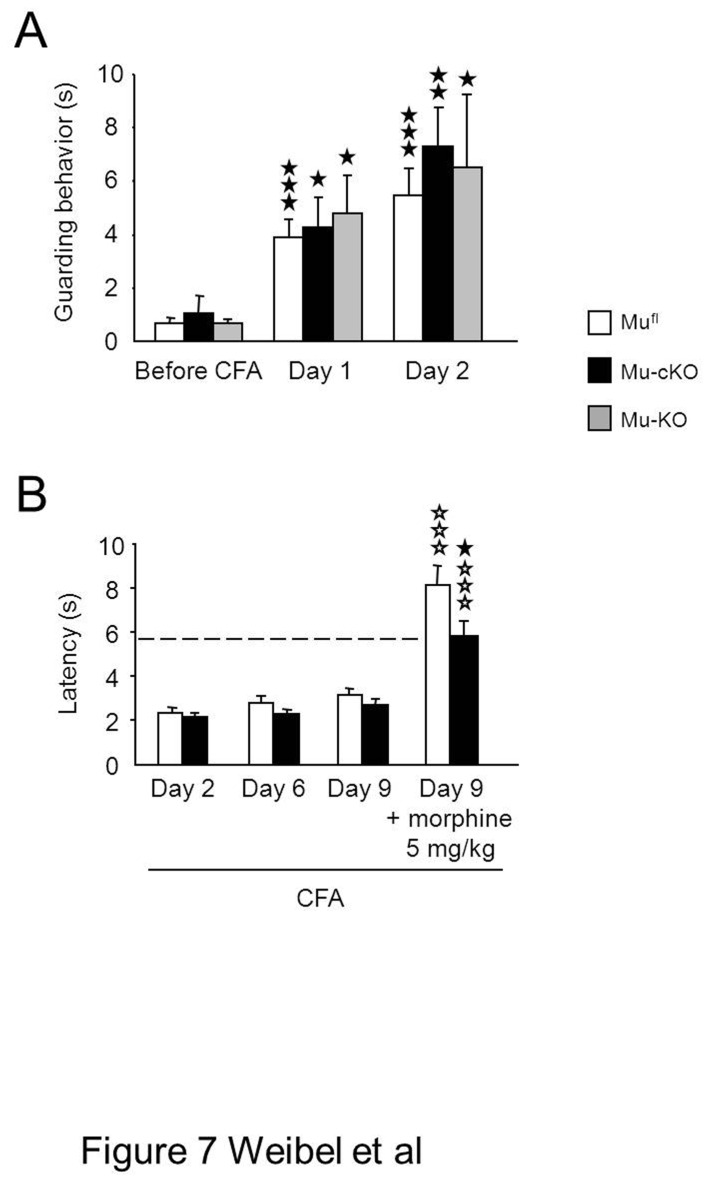
Figure 7. Spontaneous guarding pain behavior after paw-CFA and CFA-inflammatory pain at day 9 in conditional mu-cKO mice.
(A) The effect the conditional mutation on ongoing pain behavior was evaluated by quantifying the duration of guarding behavior over 6 min in mufl, mu-cKO and mu-KO mice before CFA-induced inflammation and at days 1 and 2 post-CFA. All mouse lines showed the same behavior (mufl, n=14; mu-cKO, n=6; mu-KO, n=12). Results are expressed as means ± sem. ★ P<0.05, ★★ P<0.01, ★★★ P<0.001 post-CFA vs naïve. (B) Following CFA injection into tail, mu-cKO and mufl mice showed similar heat hyperalgesia at days 2, 6 and 9. The dashed line represents baseline (pre-CFA) sensitivity in the tail immersion tests at 48°C. Morphine (i.p.) produced anti-hyperalgesia in both genotypes, and that was reduced in mu-cKO mice as compared to controls. n=19/genotype., two-way ANOVA (genotype x treatment F(1,71) = 48.812, P <0.001 for treatment; F(1,71) = 5.999, P <0.05 for genotype. Post-hoc Bonferroni test, ✰✰✰ P<0.001, morphine vs saline; ★ P<0.05, cKO vs flox controls.