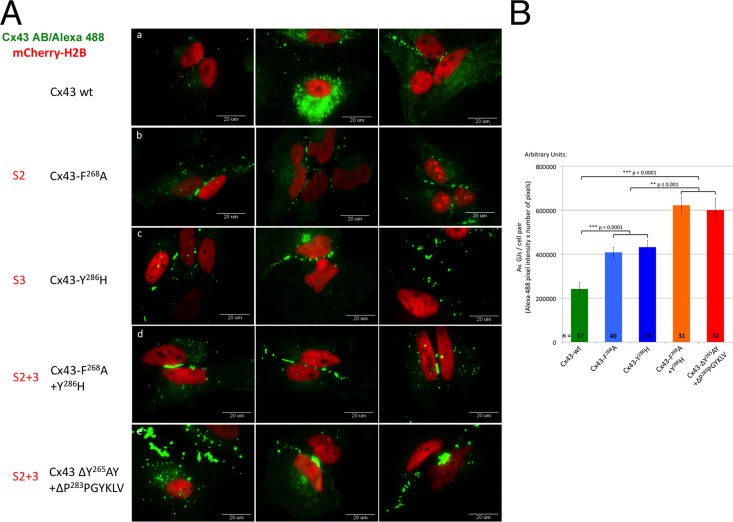
FIGURE 4:
AP-2 binding–deficient Cx43 mutants have more GJ channels in their apposed PMs. (A) Untagged wild type and S2, S3, and S2+3 Cx43 mutants were cotransfected with mCherry-H2B (red; to better reveal transfected cell pairs) into HeLa cells. Cx43 was stained for immunofluorescence analyses using primary rabbit anti-Cx43 and secondary goat anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 488 (green) labeled antibodies. Images of transfected cell pairs were acquired using a 60× oil-immersion objective. Three representative images of wild type (a) and selected mutants (b, F268A [S2]; c, Y286H [S3]; d, F268A+Y286H [S2+3]; e, ΔY265AY+ΔP283PGYKLV [S2+3]) are shown. (B) Quantitative analyses of the number of GJ channels present in apposing PMs (performed by measuring PM localized Alexa Fluor 488 fluorescence intensity of wild type and selected S2, S3, and S2+3 mutants) revealed a twofold increase in Cx43-F268A (S2) and Cx43-Y286H (S3) mutants (blue bars) and a threefold increase in Cx43-F268A+Y286H and ΔY265AY+ΔP283PGYKLV (S2+3) mutants (orange/red bars) compared with wild-type Cx43–expressing cells (green bar).