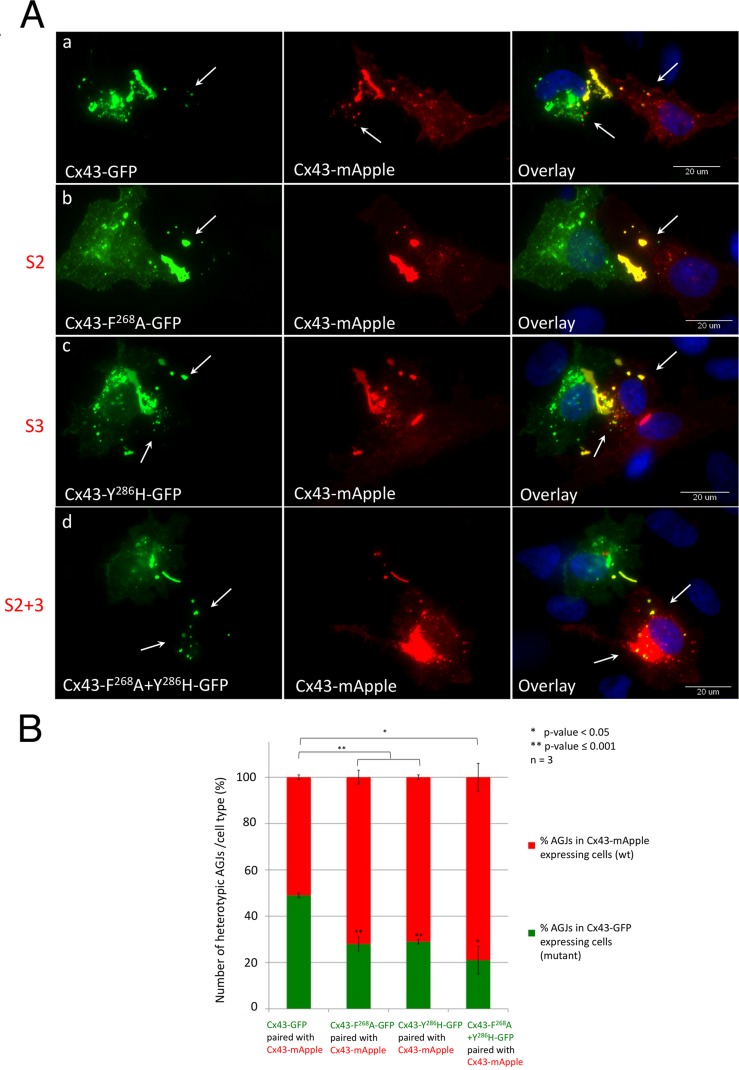
FIGURE 7:
AP-2 binding–deficient Cx43 mutants become donor cells. (A) HeLa cells were separately transfected with wild-type Cx43-mApple (red) or GFP-tagged wild type, S2, S3, or S2+3 mutant constructs (green) and cocultured. Cell pairs of wild-type Cx43-mApple and mutant/wild-type-GFP–expressing cells assemble heterotypic GJs (yellow in the overlays). Heterotypic AGJs (also appearing yellow) are depicted with arrows. Representative images of wild-type Cx43-GFP (a), F268A-GFP (b, S2), Y286H-GFP (c, S3), and F268A+Y286H-GFP (d, S2+3)–expressing cells paired with wild-type Cx43-mApple–expressing cells of three independent experiments are shown. (B) Heterotypic AGJs were counted, and their cellular location in wild-type Cx43-mApple–expressing cells vs. mutant Cx43-GFP–expressing cells was quantified. Cx43 wild-type/wild-type cell pairs exhibited an unbiased average ratio of 1:1 (bar 1), while Cx43 mutants (S2, S3, or S2+3, bars 2–4) were progressively inefficient in internalizing their plaques. Significance values between cell-pair groups, and between cell types within groups compared with wild-type/wild-type pairs are shown above and within columns, respectively.