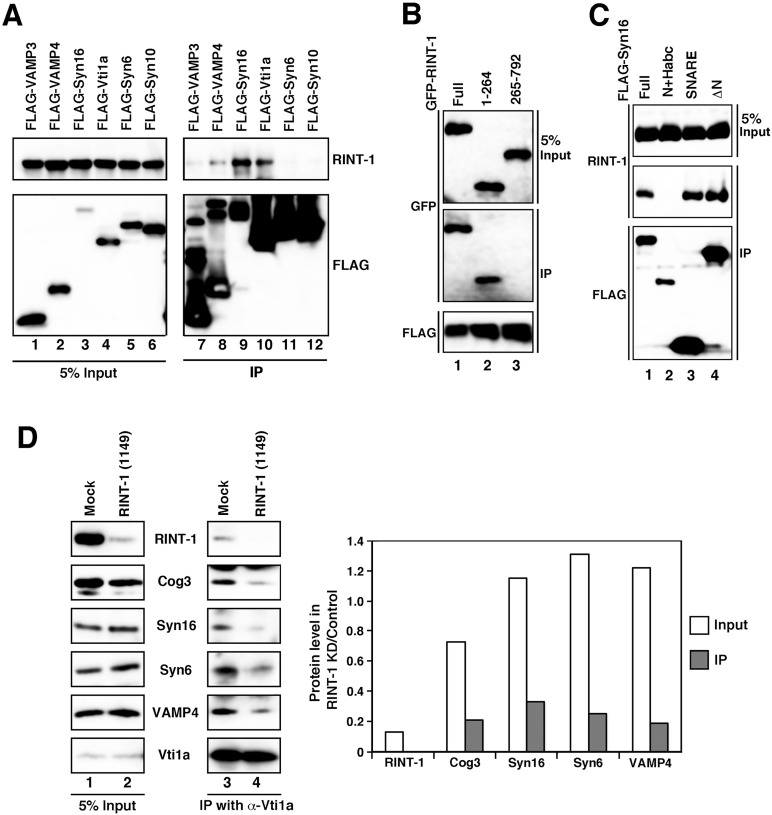
FIGURE 6:
RINT-1 modulates TGN SNARE complex assembly. (A) Lysates of cells expressing each of the FLAG-SNARE constructs were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG-beads (lanes 7–12) and analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against RINT-1 (top) and FLAG (bottom). Five percent input was also analyzed (lanes 1–6). (B) Interaction between RINT-1 and syntaxin 16. Lysates of cells expressing FLAG–syntaxin 16 and each of the GFP–RINT-1 constructs were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG beads and analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against GFP (middle) and FLAG (bottom). Five percent input was also analyzed by immunoblotting with an anti-GFP antibody (top). (C) SNARE domain is responsible for the interaction with RINT-1. Lysates of cells expressing each of the FLAG–syntaxin 16 constructs were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG beads and analyzed by immunoblotting against RINT-1 (middle) and FLAG (bottom). Five percent input was also analyzed by immunoblotting with an ant-RINT-1 antibody (top) (D) TGN SNARE complex assembly is abrogated in RINT-1–depleted cells. HeLa cells were mock transfected (lanes 1 and 3) or transfected with RINT-1 (1149) (lanes 2 and 4). At 72 h after transfection, cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti-Vti1a antibody and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies (lanes 3 and 4). Five percent input was also analyzed (lanes 1 and 2). The intensities of immunostained bands were quantitated with ImageJ. The quantitative data represent the average of two independent experiments.