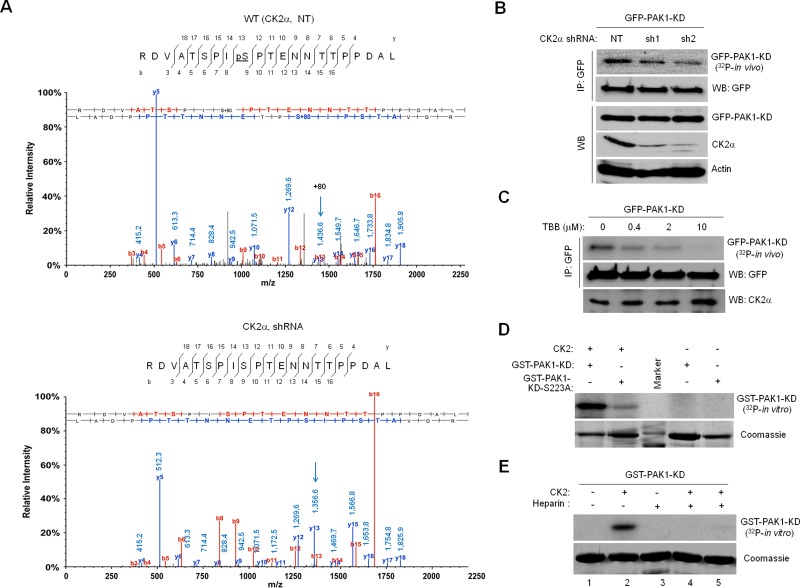
FIGURE 1:
CK2 phosphorylates PAK1 on S223. (A) Mass spectrometry identification of CK2-catalyzed PAK1 phosphorylation at S223. The 293T cells treated with a nontargeting shRNA (NT, top) or a CK2α-specific shRNA (shRNA, bottom) were infected with lentivirus expressing GFP-PAK1. GFP-PAK1 was immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibody, resolved by SDS–PAGE, and digested with trypsin or chymotrypsin/elastase. The resulting eluted peptides were analyzed directly by LC-MS/MS. The m/z difference between y-13s (arrows) of the peptides derived from 293T cells with (bottom) or without (top) CK2α knockdown indicates a phosphoserine at position 223. (B) Effect of CK2α knockdown on PAK1 phosphorylation in vivo. Western blot analysis of expression of GFP-PAK1-KD, CK2α, and actin in 293T cells with (sh1 and sh2) or without (NT) CK2α knockdown (WB). The 293T cells expressing GFP-PAK1-KD were metabolically labeled with [32P]orthophosphate. GFP-PAK1-KD was immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibody and analyzed by autoradiography. (C) Effect of the CK2 inhibitor TBB on PAK1 phosphorylation in vivo. The 293T cells expressing GFP-PAK1-KD were treated with different concentrations of TBB, as indicated above each lane, and metabolically labeled with [32P]orthophosphate. (D) In vitro phosphorylation of PAK1 by CK2. Bacterially expressed GST-PAK1-KD or GST-PAK1-KD-S223A was incubated with purified CK2 holoenzyme (20 ng) and [32P]γ-ATP and analyzed by autoradiography. (E) Effect of the CK2 inhibitor heparin on PAK1 phosphorylation in vitro. Bacterially expressed GST-PAK1-KD was incubated with purified CK2 holoenzyme (20 ng) and [32P]γ-ATP in the absence and presence of different amounts of heparin (lane 3: 25 μg; lane 4: 5 μg; lane 5: 1 μg) for 30 min and analyzed by autoradiography.