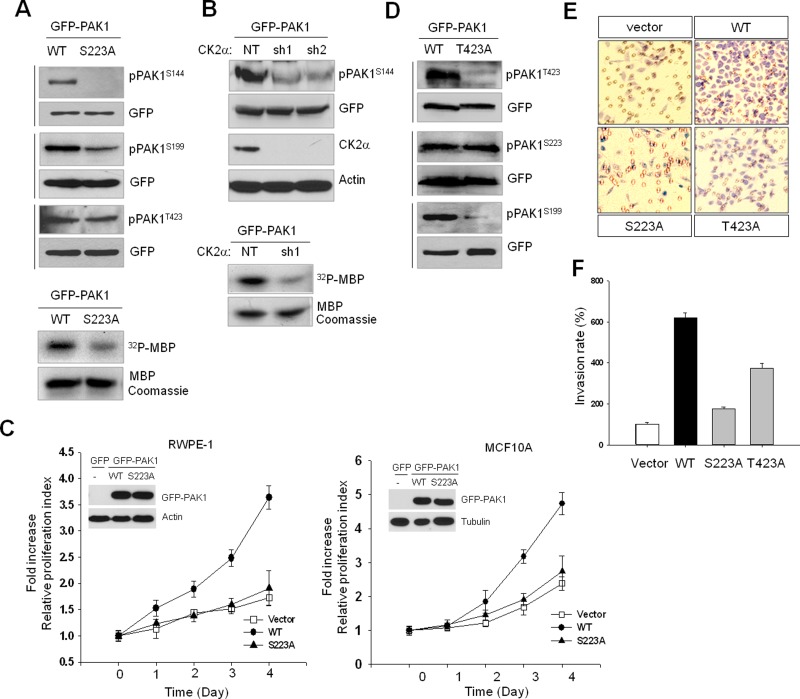
FIGURE 2:
CK2-catalyzed PAK1S223 phosphorylation is required for autophosphorylation and activity of PAK1. The 293T cells were transiently transfected with wild-type or mutant PAK1 protein, and cell extracts were subjected to Western blot analysis with phospho-specific PAK1 antibodies. The same blots were stripped and reprobed with anti-GFP antibody to control for equal protein loading. (A) Western blot analysis of phosphorylation of S144, S199, and T423 of GFP-PAK1 (WT) or GFP-PAK1S223A. The kinase activity of PAK1 (GFP-PAK1 [WT]) and GFP-PAK1S223A) was assessed by in vitro phosphorylation assay using MBP as a substrate (bottom). (B) Western blot analysis of phosphorylation of GFP-PAK1 expressed in 293T cells with (sh1 and sh2) or without (NT) CK2α knockdown with anti-pPAK1S144 antibody (pPAK1S144). Top, Western blot analysis of expression of CK2α (CK2α). Actin was used as a loading control (Actin). Bottom, in vitro phosphorylation of MBP by GFP-PAK1 immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibody from extracts of 293T cells with (sh1) or without (NT) CK2α knockdown. (C) MTT proliferation assays of RWPE-1 (left) and MCF 10A (right) cells. Cell viability over time was expressed as fold increase over untreated control at day 1. Error bars represent mean ± SD (n = 5). Insets: Western blot analysis of expression of GFP-PAK1 (WT) or GFP-PAK1S223A. (D) Western blot analysis of phosphorylation of T423, S223, and S199 of GFP-PAK1 (WT) or GFP-PAK1T423A. (E) PAK1-induced cell invasion. The benign prostate RWPE-1 cells infected with lentivirus expressing the vector plasmid, GFP-PAK1 (WT), GFP-PAK1S223A (S223A), or GFP- PAK1T423A (T423A) were used for invasion assays. (F) The invasion rate was determined by counting the cells that migrated through BME-coated inserts in the Transwell Boyden chamber and expressed as the percentage relative to control (vector). Each bar represents the mean ± SD of five fields counted.