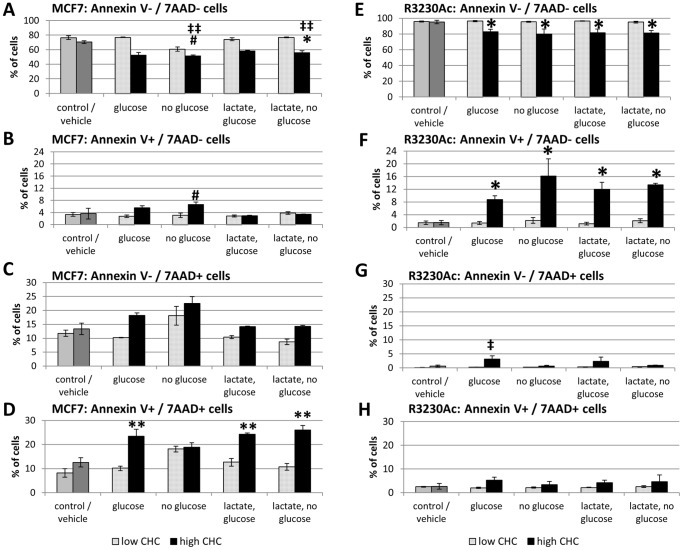
Figure 6. 24 h exposure to 5.
Cell viability as measured by Annexin V –/7-AAD – labeling (n = 3) in MCF and R3230Ac cells treated with high (5 mM) or low (0.1 mM) CHC with and without glucose (no lactate) and with 40 mM lactate (with and without glucose). Viable MCF7 cells show significant decreases with 5 mM CHC (A, #p≤0.004 compared to control (no CHC, no lactate + glucose), ‡‡p < 0.01 compared to 40 mM lactate-treated MCF7 cells, *p = 0.003 compared to all no CHC and low CHC groups). Percentage of apoptotic (Annexin V+/7-AAD-) MCF7 cells show significant increases with the –glucose-lactate+high CHC treatment and the +glucose+lactate+high CHC treatment (#p < 0.05) and between the –glucose–lactate+high CHC group and 40 mM lactate treatments without CHC (+ or – glucose) (†p < 0.05, B). Percentage of MCF7 cells with loss of membrane integrity (Annexin V–/7-AAD+) show no significant differences with CHC treatment (C). Percentage of MCF7 cells marked for both cell death pathways (Annexin V+/7-AAD+) show significant increases with 5 mM CHC compared to the no CHC and low CHC groups (**p < 0.05, D). Percentage of viable R3230Ac cells show significant decreases with 5 mM CHC compared all no CHC and low CHC groups (*p < 0.008, E). Percentage of apoptotic (Annexin V+/7-AAD-) R3230Ac cells show significant increases with 5 mM CHC compared to compared to no CHC and low CHC groups (*p < 0.02, F). Percentage of R3230Ac cells marked for loss of membrane integrity (Annexin V–/7-AAD+) show no significant differences except–glucose-lactate+high CHC treatment (‡p < 0.05, G). Percentage of R3230Ac cells marked for both cell death pathways (Annexin V+/7-AAD+) show no significant changes with any treatment (H). Results analyzed with One-Way ANOVA and Bonferroni/Dunn post-hoc tests.