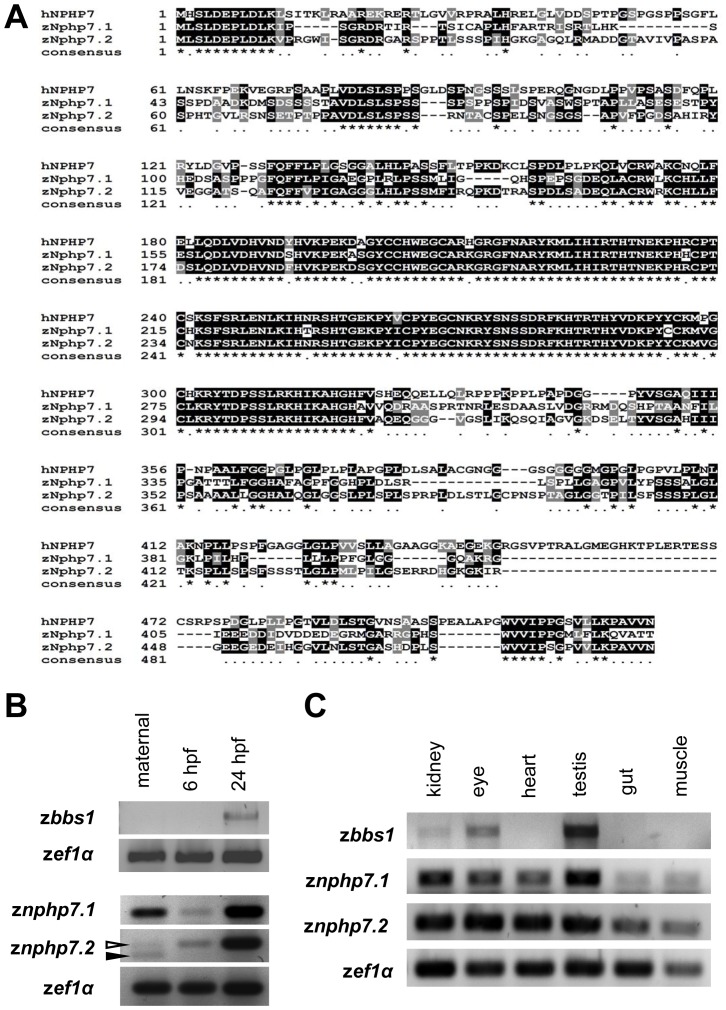
Figure 2. Expression of zbbs1 and znphp7.
(A) Identification of 2 NPHP7 homologues in zebrafish: Zebrafish Nphp7.1 (zNphp7.1) and zebrafish Nphp7.2 (zNphp7.2) consist of 446 and 489 amino acids respectively. Amino acid sequence alignment showed that zNphp7.1 shares 43.9% identity and 50.8% similarity with the human NPHP7/GLIS2 (hNPHP7); zNphp7.2 was 51.4% identical and 60.2% similar to the human homologue. The ZF domains of zNphp7.1 and zNphp7.2 were 89.3% and 91.3% identical with those of the human homologue, respectively. (*, completely conserved; ., identical in 2 sequences or belonging to same type of amino acid group in 2 or 3 sequences) (B) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR reveals maternal transcript expression for znphp7.1 and znphp7.2 whereas zbbs1 is not expressed maternally nor at 6 hpf. 2 maternal splice products were identified for znphp7.2 (open arrowhead: Transcript 1; filled arrowhead: Transcript 2). The transcript 2 of znphp7.2 is expressed only maternally. Sequencing of the lower splice product revealed an excision of 18 bp corresponding to amino acid (aa 101–118) (Fig. S1). (C) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR with organ specific cDNA from adult zebrafish indicated that zbbs1 is expressed in kidney, eye and testis. znphp7.1 and znphp7.2 are expressed in other organs including kidney, eye, heart, testis, gut and muscle.