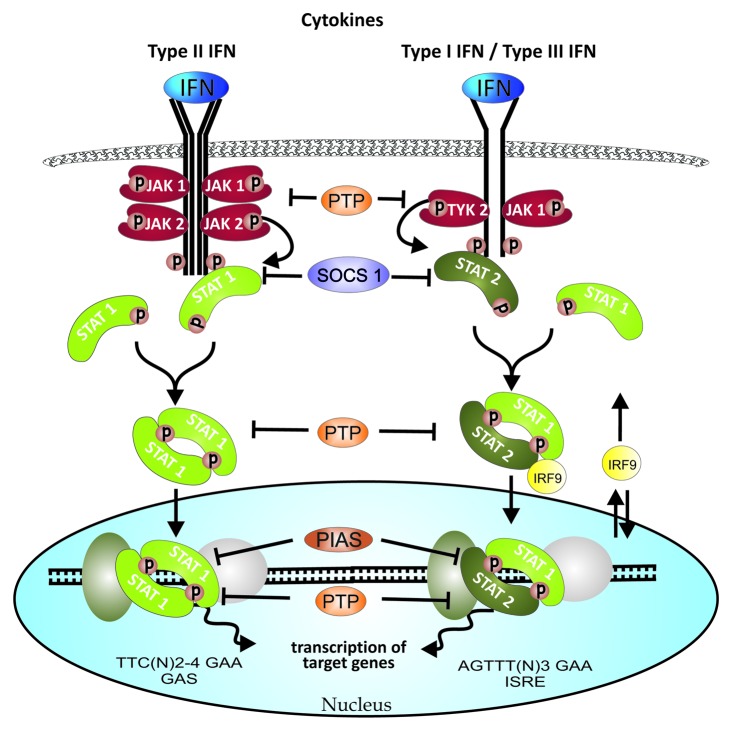
Figure 2. Key steps of JAK-STAT signaling in response to IFNs. IFNs induce activation of JAKs, receptors and subsequently, of cytoplasmic STATs; all by phosphorylation. Active STATs essentially form dimers, which then are translocated to nucleus where they act as transcription factors in the specific gene promoter or enhancer regions. IFN signaling negative regulators include multiple cytoplasmic PTPs, nuclear PTP and PIAS proteins, as well as specific to IFN signaling SOCS1 which in principle inhibits STAT1 phosphorylation process. See text for more details.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.