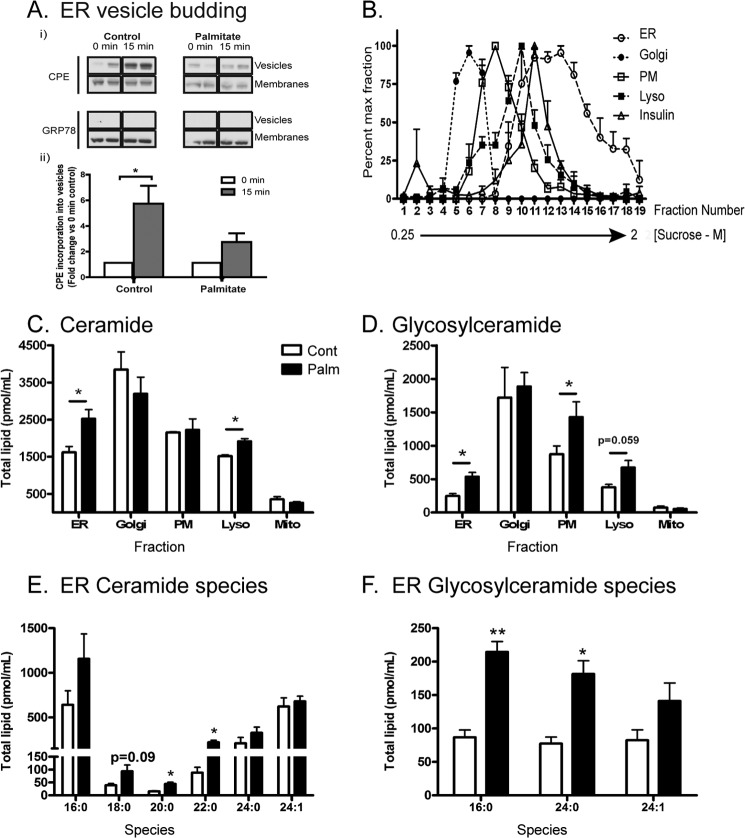
FIGURE 2.
Subcellular changes in MIN6 cells because of palmitate treatment (48 h) include inhibition of ER vesicle budding and enhanced ceramide accrual. A, microsomes (chiefly ER) were prepared from MIN6 cells pretreated with 0.4 mm palmitate/0.92% BSA. Isolated microsomes underwent a budding assay (see “Experimental Procedures”) to probe the rate of carboxypeptidase E (CPE) incorporation into ER vesicle buds over 15 min. Grp78/BiP (excluded from buds) was used as a negative control. Results are presented as representative blots (each condition in duplicate) from a total of three independent experiments (i) or as densitometry relative to 0-min control (n = 3) (ii). B, MIN6 cells were pretreated with 0.4 mm palmitate/0.92% BSA (48 h) before lysis and fractionation. The position of subcellular peaks within the sucrose gradient corresponding to the ER, Golgi, plasma membrane (PM), lysosome (Lyso), and insulin granules as characterized by organelle markers (see “Experimental Procedures”). C, mass spectrometry of total ceramide and glycosylceramide (D) content from peak fractions corresponding to each compartment and expressed as total lipid per milliliter of sucrose fraction extract. Peak fractions are as follows: ER, 13–18; Golgi, 5–8; lysosome, 11–12; and plasma membrane, 9–10. Mitochondria (Mito) were isolated separately (see “Experimental Procedures”). Cont, control; Palm, palmitate. The specific ER ceramide (E) and glycosylceramide (F) species accumulating in response to palmitate are detailed. Data represent mean ± S.E. from three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05, unpaired Student's t test compared with control condition.