FIGURE 8.
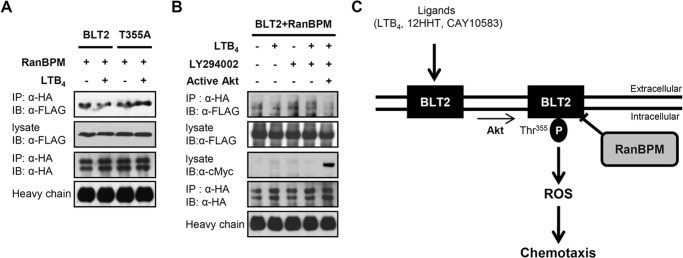
Ligand stimulation decreases the interaction between RanBPM and BLT2 via an Akt-dependent mechanism. A, 3×FLAG-RanBPM and HA-BLT2 or 3×FLAG-RanBPM and the HA-BLT2 T355A mutant were transiently co-transfected into HEK 293T cells. At 48 h after transfection, the transfected cells were exposed to control buffer (−) or 300 nm LTB4 (+) for 15 min, and immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed using an anti-HA antibody followed by Western blotting (IB) with an anti-FLAG antibody. B, 3×FLAG-RanBPM, HA-BLT2, and pUSEamp vector (control vector; −) or 3×FLAG-RanBPM, HA-BLT2, and active Akt (pUSEamp-Myr-Akt; +) (11) were transiently co-transfected into HEK 293T cells. At 48 h after transfection, the transfected cells were exposed to control buffer (−) or 300 nm LTB4 (+) for 15 min in the presence of DMSO (−) or 20 μm LY294002 (+), and immunoprecipitation was performed using an anti-HA antibody followed by Western blotting with an anti-FLAG antibody. Also, the cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-c-Myc antibody to active Akt. The data are representative of three independent experiments with similar results. C, schematic model depicting the role of RanBPM in BLT2 signaling. P indicates phosphorylation.
