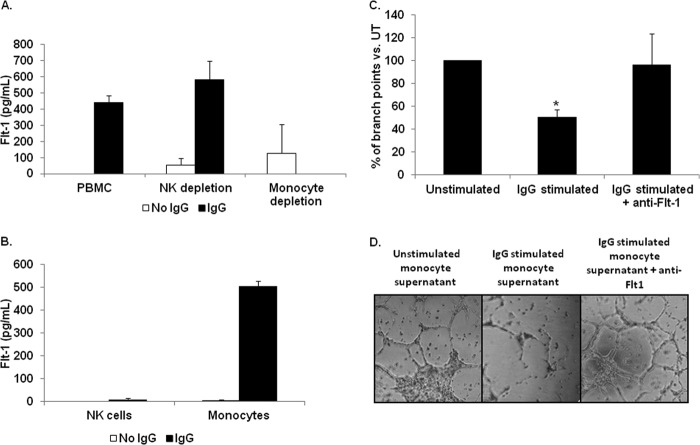
FIGURE 2.
Peripheral blood monocytes are responsible for biologically active sFlt-1 production following FcγR stimulation. To determine which FcγR bearing leukocyte(s) is capable of mediating sFlt-1 synthesis through activation of FcγR, we examined whole PBMCs, monocyte depleted PBMCs, and NK-cell depleted PBMCs by incubation on IgG-coated plates. A, ELISA shows sFlt-1 production by intact PBMCs, NK cell-depleted PBMCs, or monocyte-depleted PBMCs after FcγR clustering (representative donor; n ≥ 3). B, isolated monocytes and NK cells were incubated on IgG-coated plates, and secreted sFlt-1 was measured by ELISA. C and D, human PBMs were incubated with antibody-coated tumor cells, and cell-free supernatants were collected. These supernatants were then used to determine the ability of sFlt-1 to inhibit VEGF-A-induced tube formation by HUVEC cells. C, supernatants from unstimulated PBMs or PBMs stimulated with antibody-coated tumor cells were tested in a tube-forming assay using HUVEC cells. These assays were also done with or without a neutralizing antibody to sFlt-1. Graphed are the percentages of branch points compared with those treated with supernatants from unstimulated PBMs (representative donor; n = 3). D, shown are representative photographs of HUVEC cell branch points quantified in C.