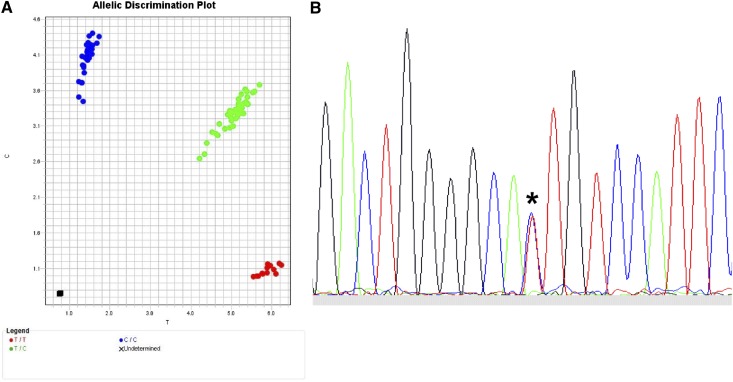
Figure 5.
Typing for SNPs. (A) TaqMan assay for typing biallelic SNPs. Actual TaqMan typing result for the G→A rs2075800 SNP (E→K at residue 602) of HSPA1L, a marker for GVHD in HLA-mismatched unrelated donor HCT.41 The assay is a real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method in which the wild-type allele is PCR-amplified separately from the alternative allele using fluorescent allele-specific probes. Shown is the allelic discrimination plot in reverse orientation: CC homozygous (blue circles; reverse orientation for GG); TT homozygous (red circles; reverse orientation for AA); and CT heterozygous (green circles). Fluorescent signals are interpreted with the use of software that detects the presence of one dye (either homozygous wild-type represented by 1 color or homozygous alternative allele represented by a different color) or 2 dyes (heterozygous wild-type and alternative allele). (B) Sequence-based typing of SNPs. Actual sequence chromatogram (reverse orientation) of a MICA*008 018-heterozygous sample illustrating the C (blue)→T (red) substitution corresponding to valine→methionine at residue 129 (*). In this sample, MICA*008 encodes valine and MICA*018 encodes methionine. Methods are previously described by Moran et al.96