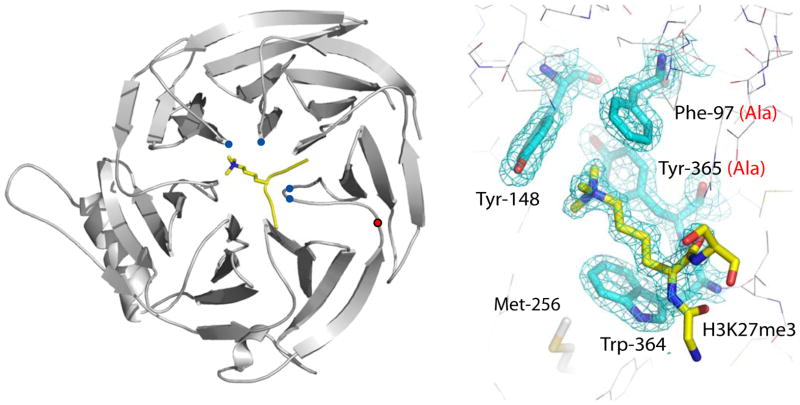
Figure 1. Trimethyl-lysine binding to an aromatic cage on Eed.
Ribbons representation of the Eed/H3K27me3 complex where Eed is coloured grey and the histone peptide is coloured yellow with its methyl-lysine side chain shown in stick representation. The Cα positions of the aromatic cage are shown as blue circles, and the Cα position of tyrosine 358 by a red circle. The bottom panel shows the methyl-lysine binding site with 2fo-fc electron density for the four cage residues and the H3K27me3 peptide. Designed mutations to the cage are shown in red in parentheses. The side-chain of methionine 256 is also shown; this is equivalent to Met-236 in esc which has been identified from classical genetic screens in Drosophila as essential for the function of Eed.