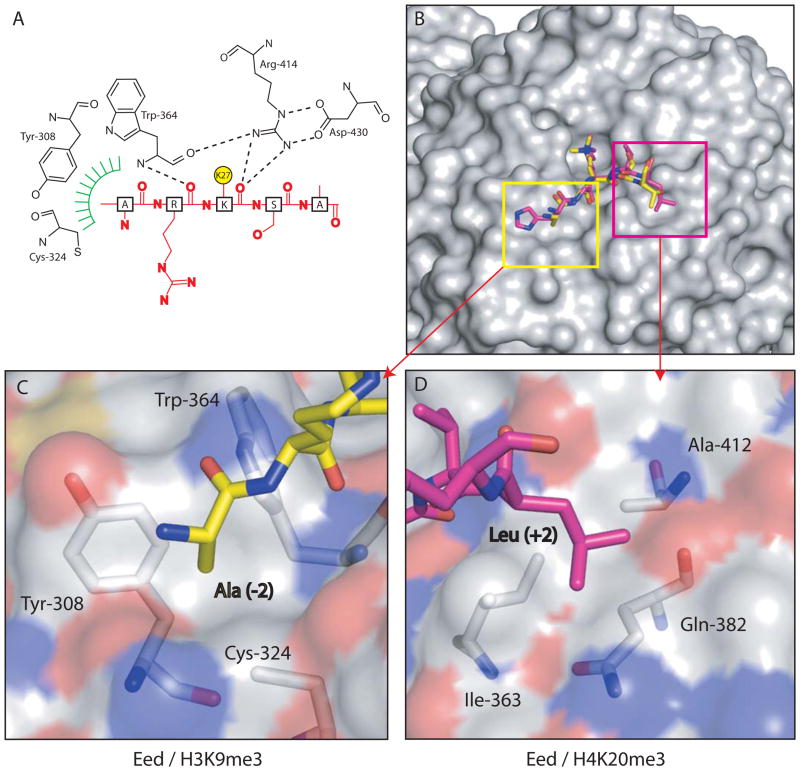
Figure 2. Interactions between Eed and trimethylated histone peptides.
(A) Schematic representation of the interaction between Eed and H3K27me3. For clarity, the aromatic methyl-lysine binding cage has been omitted and the methylated lysine side-chain shown as a yellow circle. Hydrogen bonds from the main-chain carbonyl of the methyl-lysine, and the residue immediately N-terminal to it, with Eed are shown as dashed lines. The green hatching indicates the hydrophobic pocket on EED which accommodates the alanine side chain two residues before the methyl-lysine. (B) Eed is shown in surface representation with a composite of two of its cognate peptides shown in sticks representation and coloured yellow (H3K9me3) and pink (H4K20me3). (C) shows the pocket on Eed that accommodates Ala (−2) from the H3K9me3 peptide while (D) shows the other pocket that contains and Leu (+2) from the H4K20me3 peptide. The Eed surface is coloured according to atom type.