Figure 3. Transmission of epigenetic states.
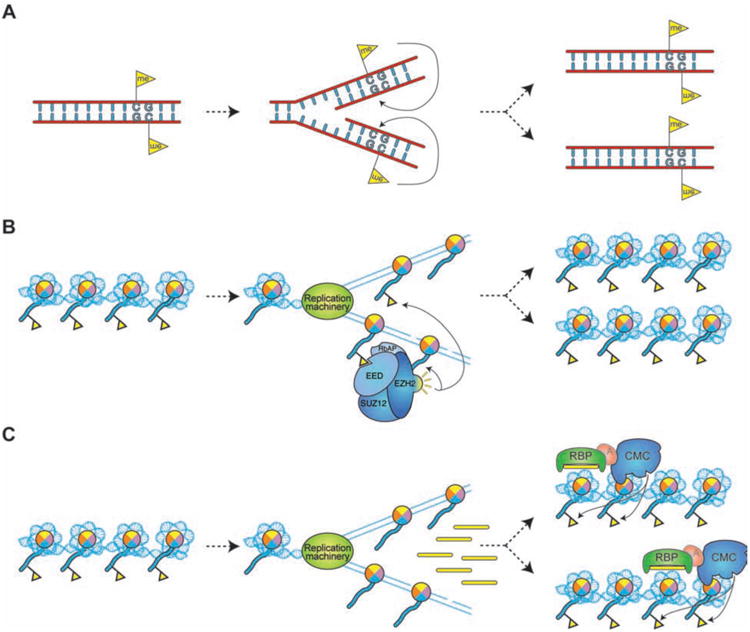
(A) Transmission of DNA methylation patterns after DNA replication. (B) Hypothetical model for the maintenance of a histone-associated epigenetic signal, using H3K27me3 (yellow flag) as an example. H3K27me3 is diluted during DNA replication by the deposition of unmodified octamers. Binding of EED to H3K27me3 stimulates the enzymatic activity of EZH2, which places more H3K27me3 marks on neighboring nucleosomes, thus restoring a full epigenetic signature on both chromatids (48). (C) Maintenance of a chromatin domain via a “secondary” signal. S phase transcription of heterochromatic repeats in S. pombe generates sRNA species that recruit chromatin-modifying complexes to reestablish heterochromatic signatures at the target loci.
