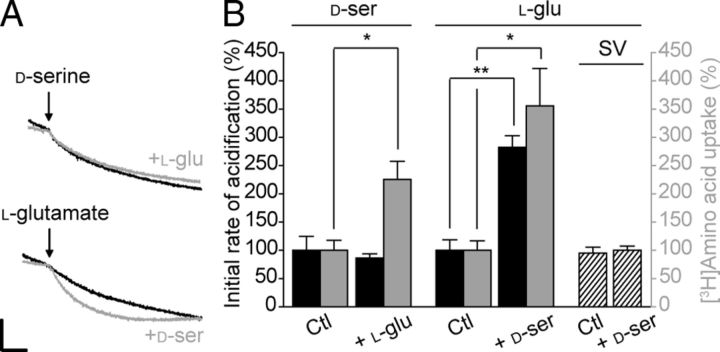
Figure 9.
Vesicular synergy between d-serine and l-glutamate transport activities in GVs. A, Partial photometric traces showing the acidification induced by 5 mm d-serine (top) and 5 mm l-glutamate (bottom) in the absence (black) or presence (gray) of 5 mm l-glutamate and 5 mm d-serine, respectively. The experiments were performed as in Figure 7, i.e., initiated with 10 mm ATP and ended with 50 mm (NH4)2SO4. Scale bar, 2 arbitrary units per 1 min. B, Histogram showing the reciprocal effect of each amino acid (d-serine or l-glutamate) on the acidification rate and uptake of the other one. Amino-acid-induced acidification was measured as in A. FCCP-sensitive ATP-dependent uptakes of l-[3H]glutamate or d-[3H]serine were measured in the presence of 10 mm d-serine or l-glutamate, respectively. Ctl, Control. Error bars represent mean ± SEM; n = 3 for acidification, 4 in duplicate for radioactive assay. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, Student's t test.