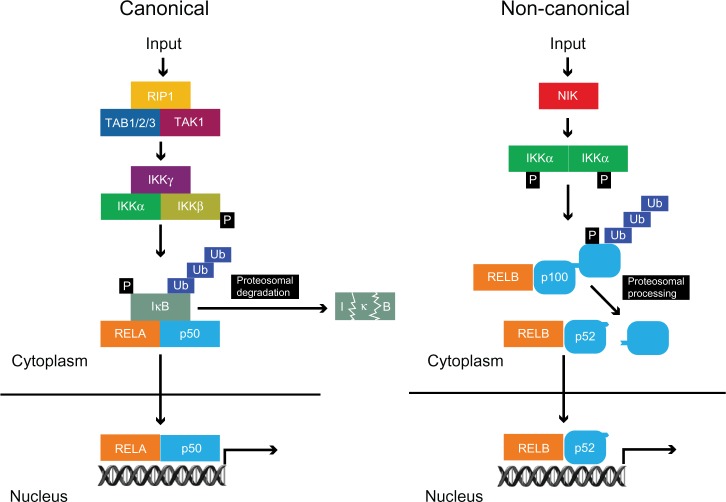
Figure 2.
Canonical and non-canonical pathways of NF-κB activation.
Notes: In the canonical pathway, a variety of inputs such as inflammatory cytokines induce the phosphorylation and activation of the IκB kinase (IKK) complex (IKKα, IKKβ, and IKKγ/NEMO). This phosphorylates IκB leading to its ubiquitination and degradation by the 26S proteasome leading to nuclear translocation of RELA:p50 dimers. The non-canonical pathway is activated by more specific inputs such as lymphotoxin-β and leads to NF-κB inducing kinase (NIK) phosphorylating and activating IKKα, a member of the multi-subunit IκB kinase complex. This leads to phosphorylation and subsequent ubiquitination of p100 resulting in its processing by the proteosome to produce transcriptionally active RELB:p52 dimers.
Abbreviations: NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; REL, reticuloendotheliosis virus; RIP, receptor-interacting serine/threonine protein kinase 1; TAB, transforming growth factor-beta activated kinase binding protein; TAK, transforming growth factor-beta activated kinase; Ub, ubiquitin.