Figure 3. Flow chart illustrating the proposed 2-level classification scheme for subjects with AOS, agrammatic aphasia, or both.
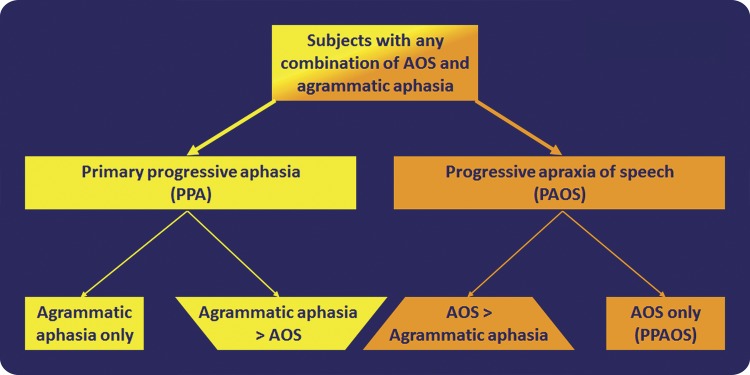
Subjects with agrammatic aphasia, AOS, or both should be first separated into those with PPA and those with PAOS. The diagnosis of PPA (specifically agPPA) should be made in those with either isolated agrammatic aphasia or dominant agrammatic aphasia, i.e., if AOS is present, it must be less severe than the aphasia. Similarly, the diagnosis of PAOS should be made in those with either isolated AOS or dominant AOS, i.e., if aphasia is present, it must be less severe than the AOS. agPPA and PAOS can then be further subdivided. Specifically, for agPPA, those with isolated agrammatic aphasia can be separated from those in which the aphasia is more severe than the AOS, and for PAOS, those with isolated AOS (PPAOS) can be separated from those in which the AOS is more severe than the aphasia (dominant AOS). agPPA = agrammatic PPA; AOS = apraxia of speech; PPAOS = primary progressive AOS.
