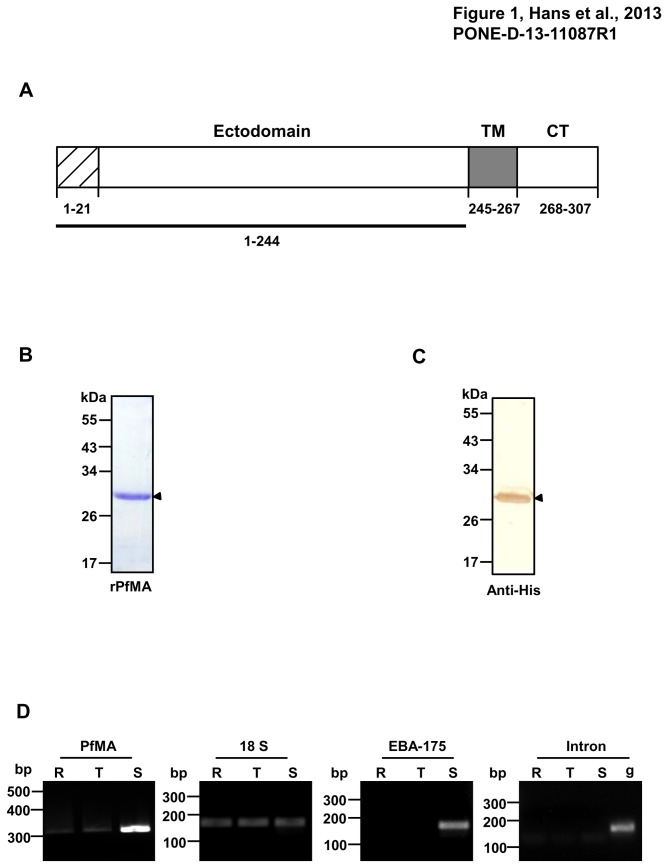
Figure 1. Expression of recombinant PfMA and transcriptional analysis of PfMA in different blood stages of P. falciparum.
(A) Schematic representation of the primary structure of the 307 amino acid PfMA protein (PlasmoDB ID PF3D7_0316000). PfMA comprises of an N-terminal hydrophobic stretch (residues 1 to 21), a transmembrane TM domain (residues 245-267), and a cytoplasmic tail (CT) at the carboxyl terminal (residues 268-307). The ectodomain (1-244 residues) was expressed in a recombinant form (shown as a bar) and antibodies were raised to this region. (B) SDS-PAGE showing purified recombinant PfMA (rPfMA) at the expected size of 30kDa (shown with arrow). (C) Detection of rPfMA by anti-polyHistidine tag antibody (Sigma) by immunoblotting (shown with arrow) (D) RT-PCR analysis of PfMA in different blood stages of P. falciparum cDNA prepared from different blood stages i.e. ring (R), trophozoite (T) and schizont (S) were used to amplify PfMA transcripts using gene specific primers. The level of PfMA transcription increased from the ring to schizont stages. As a control for equal amounts of RNA from the three stages, RT-PCR was performed with the 18S rRNA primers. RT-PCR of EBA-175 was analyzed as a control for stage specificity. Intronic primers showed amplification only in genomic DNA (g) and not in cDNA from all the stages.