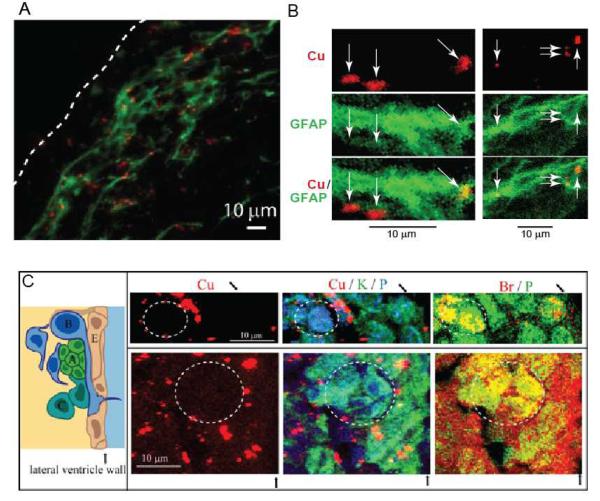
Figure 3.
A. Co-localization of optical fluorescence of immunochemically stained GFAP (green) and X-ray fluorescence from Cu (red). The white dashed line indicates the ventricle wall. B. Subcellular colocalization of Cu with GFAP as visualized by immunostaining with gold nanoparticles as a secondary antibody. C. Left: Schematic of the cellular architecture of the SVZ. Progenitor cells (A-C) in the SVZ lie adjacent to the ependymal cell (E) layer lining the lateral ventricles. Right: μXRF image of cells located in the SVZ of a Sprague–Dawley rat treated with BrdU – a marker of actively dividing cells. BrdU identifies type A cells - migrating neuroblasts and type C cells - transit amplifying cells. Co-localization of Br and phosphorus X-ray fluorescence signals shows actively dividing cells (dashed circles). Areas occupied by dividing cells have a diminished number of Cu-accumulations. The black arrows indicate the ventricle wall.