Fig. 1. Activities of RGENs harboring variant mismatched sgRNAs in a human cell-based EGFP disruption assay.
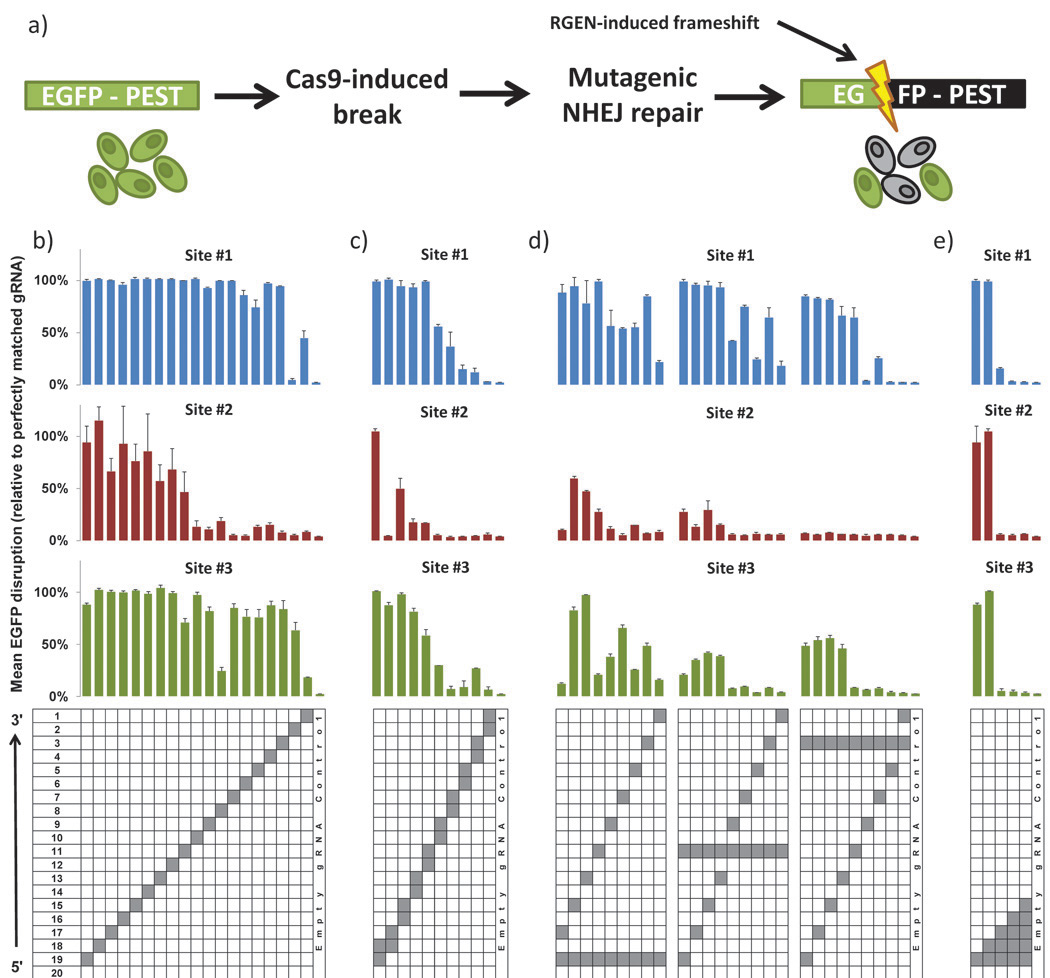
(a) Schematic overview of the EGFP disruption assay. Repair of targeted Cas9-mediated double-stranded breaks in a single integrated EGFP-PEST reporter gene by error-prone NHEJ-mediated repair leads to frameshift mutations that disrupt the coding sequence and to associated loss of fluorescence in cells. Activities of RGENs harboring sgRNAs bearing (b) single mismatches, (c) adjacent double mismatches, (d) variably spaced double mismatches, and (e) increasing numbers of adjacent mismatches assayed on three different target sites in the EGFP reporter gene sequence. Mean activities of replicates (see Online Methods) are shown, normalized to the activity of a perfectly matched sgRNA. Error bars indicate standard errors of the mean. Positions mismatched in each sgRNA are highlighted in grey in the grid below. Sequences of the three EGFP target sites are shown in Supplementary Figure 2a.
